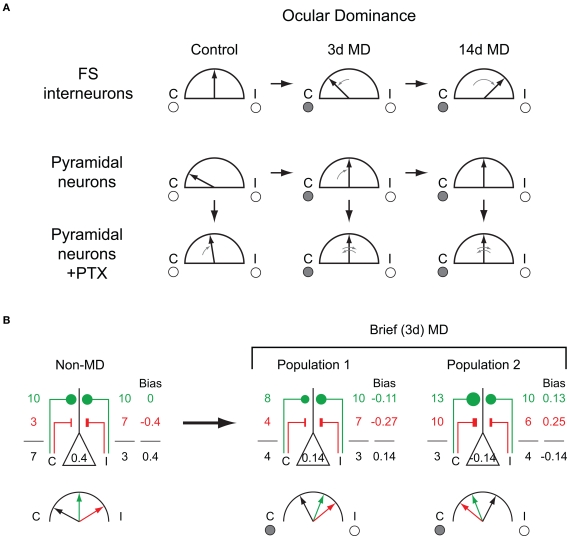
Figure 1.
Consequences of bidirectional OD plasticity in fast-spiking GABA circuits. (A) Schematic summary of OD data for FS and pyramidal neurons reported by Yazaki-Sugiyama et al. Black arrows indicate OD bias under a given condition, ranging from purely contralateral-eye responses to purely ipsilateral-eye responses. Small gray arrows indicate changes relative to control (non-MD or no PTX conditions). Top row: In non-MD mice, FS cells exhibit binocular responses, which first shift toward the deprived eye after 3 days MD, then become biased to the open-eye after 14 days MD. Middle row: Pyramidal neurons in non-MD mice display contralaterally biased responses, which become binocular following either 3 or 14 days MD. Bottom row: Spike bias in pyramidal neurons after intracellular PTX application. In non-MD mice, responses become binocular with intracellular PTX, whereas after 3 days MD PTX leads to inversion of OD biases. (B) Schematic representation of the relative strengths of excitatory and inhibitory inputs which could potentially produce the observed data. Numbers represent relative excitatory (green) and inhibitory (red) synaptic strengths of inputs driven by stimulation of the contralateral or ipsilateral eye. Number in center of pyramidal neuron is the overall spike bias, and numbers to left and right represent the influences of contralateral and ipsilateral visual stimulation, respectively. Excitatory and inhibitory inputs sum to generate the overall response and resulting spike bias. Left panel: In order to produce contralaterally biased responses in neurons receiving binocularly balanced excitation, ipsilaterally dominated inhibitory inputs (and therefore ipsilaterally dominated inhibitory neurons) are required. Right panels: After MD excitatory neurons are on average binocular, comprised of two populations showing a modest bias to either eye. These overall biases invert in the absence of inhibition, thus excitatory inputs have the opposite OD bias from the neuron itself.