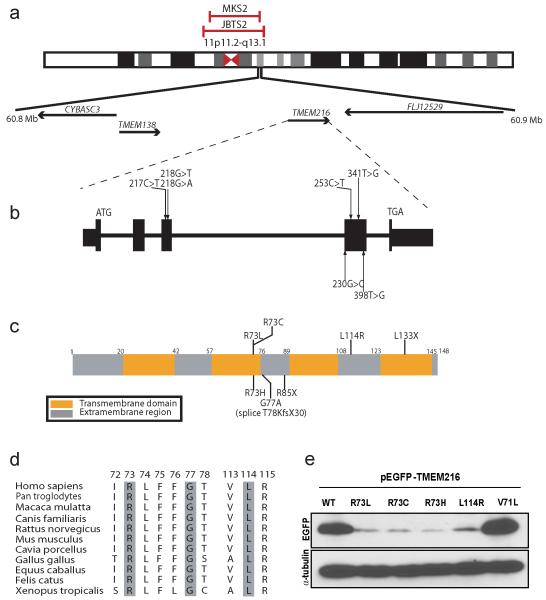
Figure 1.
Mutations in the TMEM216 gene in patients linked to the JBTS2 and MKS2 loci. (a) Chromosomal location of the JBTS2 and MKS2 loci on Chr. 11cent. (b) TMEM216 genomic organization, depicting start and stop codon, and location of identified base changes. (c) The longest splice isoform encodes for a 148 aa tetraspan membrane protein. Patient mutations predominate towards the middle, with one prevalent p.R73 change occurring repeatedly. Missense, nonsense and splice mutations were identified. (d) Evolutionary conservation of mutated amino acids. (e) Patient mutations lead to unstable protein products. Western blot of whole lysate of cells transfected with a cDNA encoding wild type (WT) vs. patient missense mutations, compared with control (p.V71L). Each mutation resulted in the production of 40-50% of WT protein levels, compared with α-tubulin loading control.