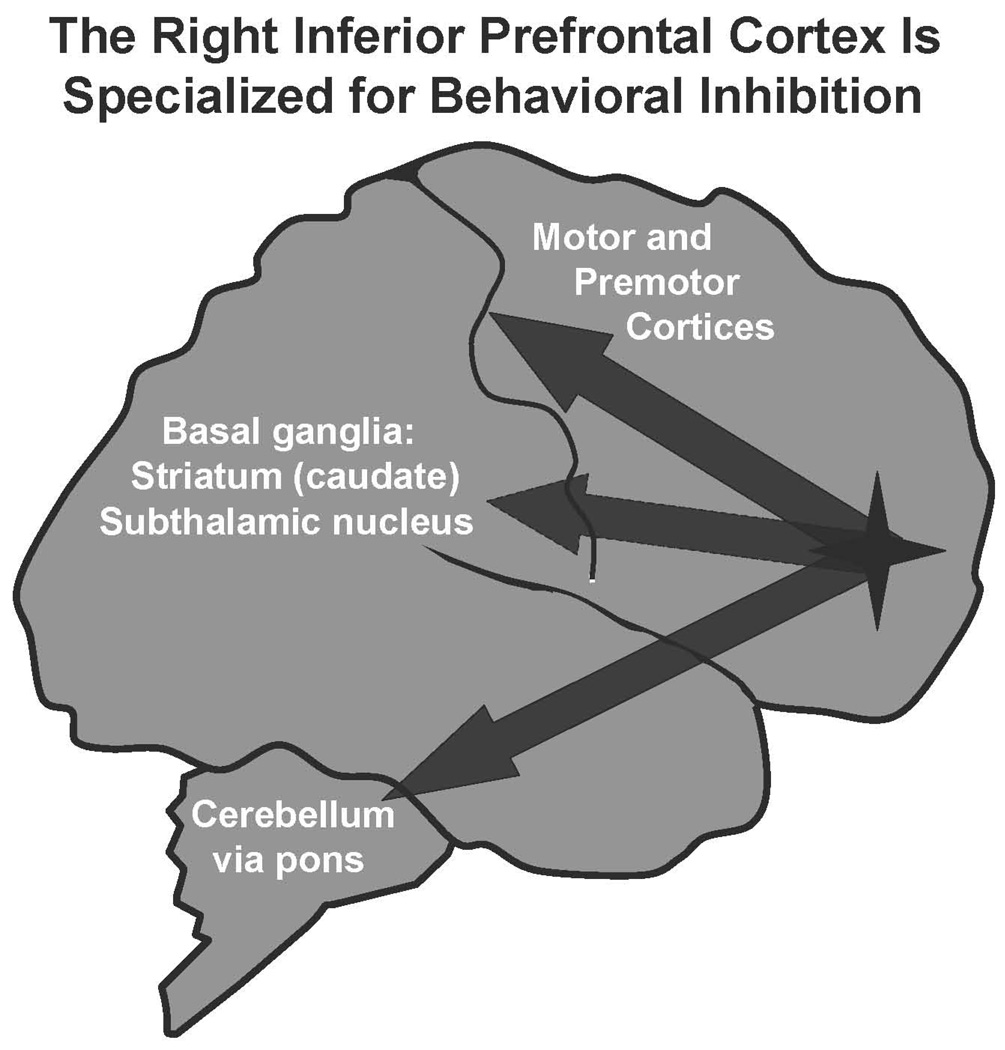
Figure 2.
The PFC regulates behavior and inhibits inappropriate impulses. In humans, the right inferior PFC is specialized for behavioral inhibition. Projections from this area to the premotor and motor cortices, the basal ganglia (striatum and subthalamic nucleus), and the cerebellum (by way of the pontine nuclei) are likely involved in the inhibition of inappropriate movements and impulses. In monkeys, blockade of alpha-2A receptors in the PFC induces a pattern of impulsive responding and locomotor hyperactivity.68,69