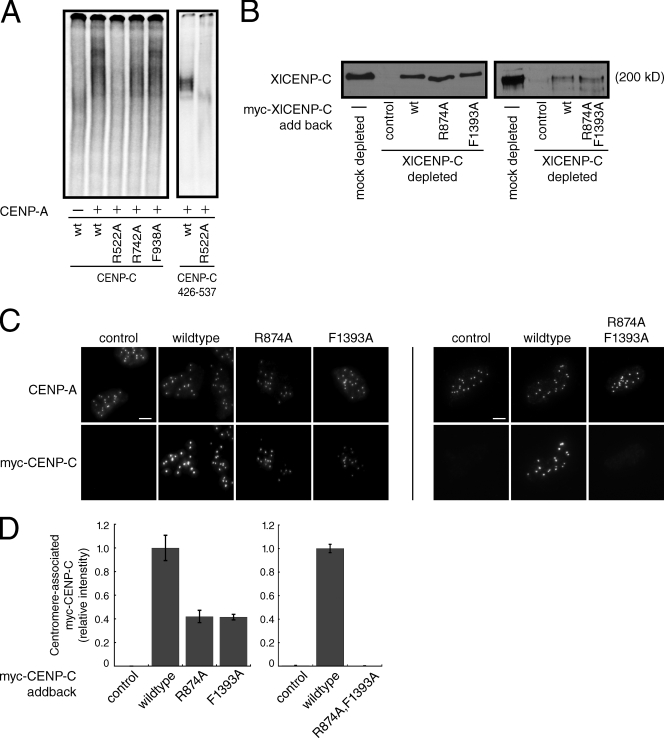
Figure 3.
A conserved arginine residue within CENP-C is required for nucleosome binding and centromere localization. (A) Wild-type (wt) human CENP-C or the indicated point mutant was incubated alone (−) or with CENP-A nucleosomes (+) and resolved on a native gel (left). Alternatively, the wild-type (wt) or R522A CENP-C426–537 fragments were incubated with CENP-A nucleosomes (10 nM). (B) Western blot using an anti–XlCENP-C antibody of mock-depleted or CENP-C–depleted Xenopus extracts containing reticulocyte-produced wild-type XlCENP-C (wt) or the indicated point mutants. Reticulocyte extract lacking myc-CENP-C (−) was used as a control. R874 and F1393 in Xenopus CENP-C are analogous to R522 and F938, respectively, in human CENP-C. The molecular weight of XlCENP-C is indicated. (C) Isolated sperm nuclei from CENP-C–depleted Xenopus extracts containing the indicated myc-CENP-C protein were stained with anti–XlCENP-A and anti-myc antibodies. Images are maximum-intensity projections of z stacks collected at 0.2-µM steps. Bars, 5 µM. (D) Quantification of centromere-associated myc-CENP-C from C. Error bars show the SEM from three independent experiments (>100 centromeres were counted for each condition in each experiment).