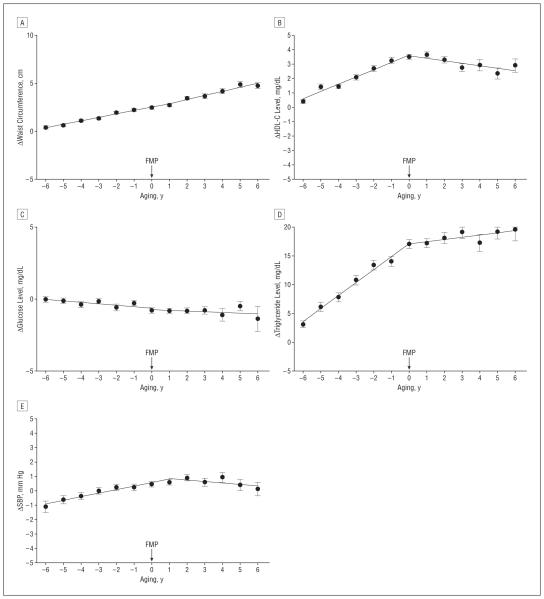
Figure 2.
Changes in components of the metabolic syndrome by aging after adjustment for standard risk factors, including baseline outcome, age at final menstrual period (FMP), ethnicity, study site, education, marital status, smoking, baseline body mass index (BMI), and change (Δ) in BMI from baseline. Components include waist circumference (A), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels (B), glucose levels (C), triglyceride levels (D), and systolic blood pressure (E). To convert glucose to millimoles per liter, multiply by 0.0555; HDL-C to millimoles per liter, multiply by 0.0259; and triglyceride to millimoles per liter, multiply by 0.0113.