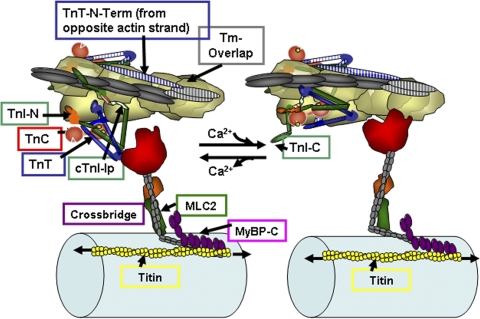
Figure 1.
A section of cardiac thin filaments illustrating the position of troponin components with Tm in the OFF state (left) and ON state (right). Thin filaments are shown containing TnI, TnT, and TnC. cTnC, a dumbbell-shaped protein with an N lobe containing a single regulatory Ca-binding site (yellow spheres) and a C lobe containing slowly exchanged Ca2+/Mg2+ sites. In the OFF state, Tm is immobile and held in place by TnI, which is shown tethered to actin on an actin strand by an Ip and a second actin-binding region flanking a switch peptide (Sw), which interacts with cTnC upon Ca activation. Note that the Ip of cTnI binds to one actin strand, whereas the N-terminal tail of TnT interacts with Tm on the adjacent actin strand. The distal C-terminal end of cTnI drapes across azimuthal actins and may interact with Tm. TnI has a unique stretch of N-terminal amino acids, which contain phosphorylation sites at S23 and S24. The N peptide interacts with the N lobe of cTnC, but it is released upon phosphorylation. With release of Ca2+, there is a release of cTnI from actin and binding of the switch peptide to cTnC. Activation is associated with release of Tm from an immobilized state by protein signaling to cTnT and possible release of Tm from an interaction with the C-terminal end of cTnI. See Are kinetic processes intrinsic to… for further description.