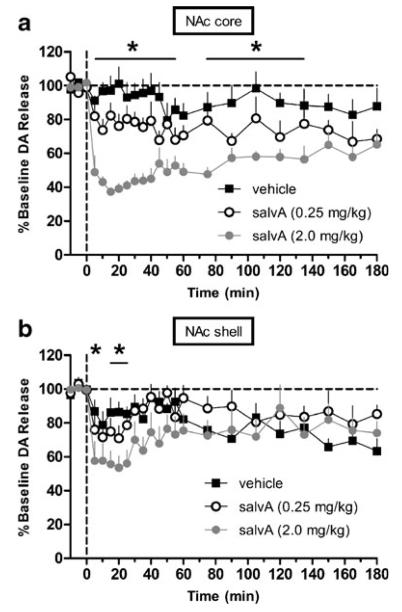
Fig. 2.
SalvA decreases phasic dopamine concentration evoked by electrical stimulation of the VTA. a) Time course of salvA effects on the peak concentration of dopamine in the NAc core evoked by electrical stimulation. Compared to vehicle (n=6 rats), salvA (2.0 mg/kg; n=6 rats) significantly decreased evoked dopamine concentration in the NAc core from 5–135, but not 60, min post-injection. Compared to vehicle, salvA (0.25 mg/kg; n=6 rats) had no effect on peak dopamine concentration. b) Time course of salvA effects on the peak concentration of dopamine in the NAc shell evoked by electrical stimulation. Compared to vehicle (n=6 rats), salvA (2.0 mg/kg; n=6 rats) significantly decreased evoked dopamine concentration in the NAc shell from 5 to 25 min with the exception of 10-min post-injection. Compared to vehicle, salvA (0.25 mg/kg; n=5 rats) had no effect on peak dopamine concentration. In both graphs, each point represents the mean (+sem) percent change from pre-injection baseline. *p<0.01 compared to vehicle at each time point, Fisher's protected t tests