Figure 7.
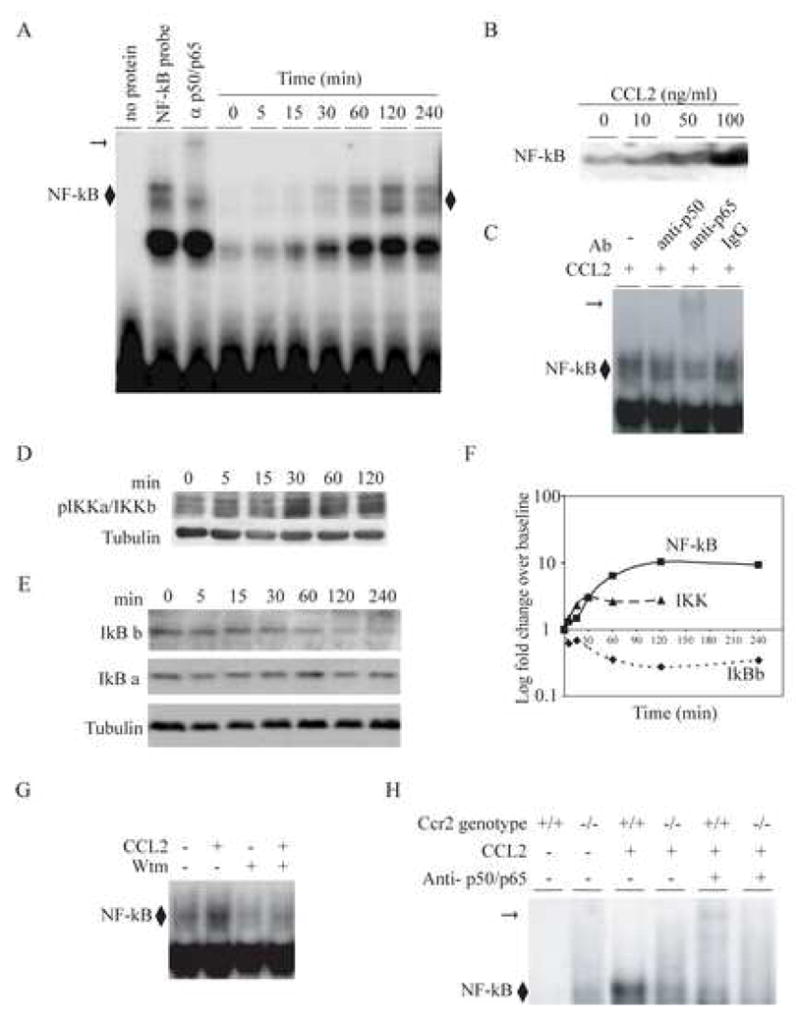
CCL2 induced activation of the NF-κB pathway in primary murine astrocytes. Astrocytes were derived from Ccr2+/+ animals. (A), Time-dependent induction of NF-κB by CCL2 (100ng/ml). Astrocytes were treated with CCL2 for the indicated time-points and nuclear extracts were prepared for EMSAs. EMSAs were conducted using a consensus NF-κB probe and supershift assays were performed using a combination of anti-p50 and -p65 antibodies (third lane). Note, supershift in the third lane indicated by the horizontal arrow. ◆, represents NF-κB bound to the probe. Maximal nuclear translocation of NF-κB was detected at 120 min, and this time interval was therefore used in the experiments shown in panels B and C. (B), CCL2 induced nuclear translocation of NF-κB in a dose-dependent manner. Primary murine astrocytes were treated with the indicated concentrations of CCL2 for 120 min and nuclear translocation of NF-κB was detected by EMSAs. (C), CCL2 induced predominantly the translocation of the p65 component of the NF-κB complex. A supershift was detected with an anti-p65 Ab, but not anti-p50 or isototype (IgG) control Ab. (D), CCL2 activated IKKα/IKKβ in astrocytes. Astrocytes were treated with CCL2 (100ng/ml) for the indicated time intervals. Cytoplasmic extracts were prepared and probed with the indicated Abs using Western blots. Anti-tubulin antibody was used to determine equal protein loading (lower panel). Maximal phosphorylation of IKKα/IKKβ was detected at 30 min. (E), CCL2-induced NF-κB translocation is associated with degradation of IκBβ but not IκBα. Cytoplasmic extracts were prepared from astrocytes treated with CCL2 for the time intervals shown and then probed with the indicated antibodies using Western blots. (F), Summary of time kinetics of signaling events that lead to CCL2 induced NF-κB nuclear translocation. Fold differences shown in panels A to E were log transformed and plotted against time. The CCL2-induced NF-κB nuclear translocation in astrocytes was dependent on PI 3 -kinase and expression of CCR2. (G), CCL2-induced nuclear translocation of NF-κB is inhibited by wortmannin (Wtm). Astrocytes were treated with 250nM wortmannin for 1 hour before stimulation with CCL2 for 2 hours. Nuclear extracts were prepared and used for EMSA. (H), CCL2-induced nuclear translocation of NF-κB was markedly diminished in Ccr2−/− astrocytes. Nuclear extracts were derived from Ccr2+/+ and Ccr2−/− astrocytes treated with CCL2 at 100 ng/ml for 120 min. Supershifts were performed with a combination of anti-p50 and -p65 antibodies.
