Fig. 3.
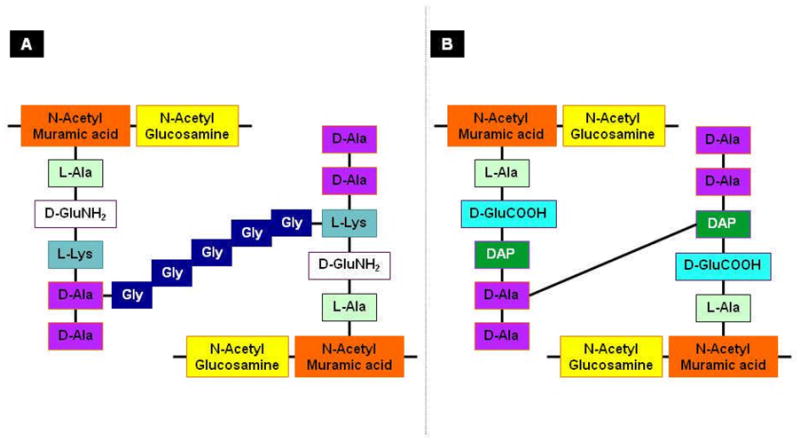
Schematic representation of the (A) S. aureus and (B) Escherichia coli murein monomers. (A) In S. aureus, N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid form the backbone of the murein. It is attached to pentapeptides containing L-alanine, D-glutamc acid, L-lysine and D-alanyl-D-alanine. The two pentapeptides are linked with a penta-glycine cross bridge. (B) In Escherichia coli, the murein backbone is composed of the same sugar moieties as S. aureus, N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid. The backbone is attached to pentapeptides containing L-alanine, D-glutamic acid, L-diaminopimelic acid and D-alanyl-D-alanine. Cross-linking occurs between diaminopimelic acid and D-alanine. The D-alanines in red boxes are usually liberated upon transpeptidation.
