Fig. 2.
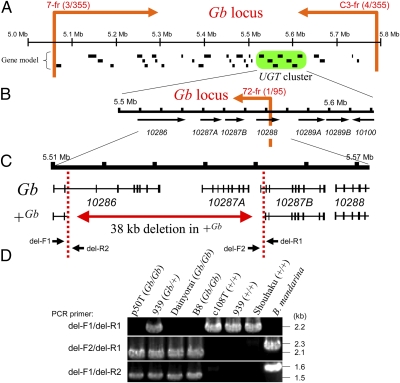
Positional cloning of Gb. (A) Physical map indicating the results of the initial linkage analysis using 355 F1 progeny obtained from a male informative cross of strain 939. The Gb locus was narrowed to the genomic region flanked by PCR markers 7-fr and C3-fr, as indicated by orange arrows with the number of recombinant animals/total number of scored individuals (Fig. S1). Putative genes predicted by Gene model program (34) are shown below map, and UGT gene cluster harboring seven UGTs (15) is highlighted in green. (B) Physical map resulting from fine mapping using 95 recombinants between Gb and q loci recovered from male informative F1 progeny (~1,700 individuals) of strain 939 (Fig. S1). Gb locus was located upstream of marker 72-fr, as indicated by orange arrow. Black arrows indicate position and orientation of transcription of seven UGTs. (C) Physical map indicating 38-kb deletion found in +Gb allele. Exons of UGTs are indicated by vertical lines. (D) Genotyping of several silkworm strains and B. mandarina for Gb. Genomic PCR was performed using primers (listed in Table S3) that flank the deletion (del-F1 and del-R1) or are located inside the deletion (del-F2 and del-R2), as shown in C. Strain names and their genotypes (in parentheses) are indicated above. Note that these PCR primers can anneal to the genome of B. mandarina and that the deletion was not found in this species.