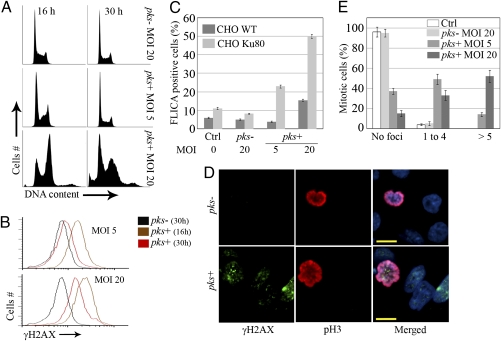
Fig. 2.
DNA damage repair, cell death, and division after low-dose infection with pks+ E. coli. CHO cells were infected for 4 h with live pks+ or pks− E. coli with an MOI of 5–20 bacteria per cell or were left uninfected (Ctrl). At the end of the infection, the cells were washed and grown with gentamicin. (A) Cell-cycle analysis 16 and 30 h after infection. (B) γH2AX levels were quantified by flow cytometry 16 or 30 h after infection. (C) CHO or xrs-6 Ku80-defective cells were infected; 24 h later, apoptotic cells were labeled with a carboxyfluorescein fluoromethyl ketone peptide inhibitor of caspases (FLICA) for 1 h and quantified by flow cytometry. Error bars represent SE from three experiments. (D) The cells were examined by confocal microscopy for DNA (blue), Ser10-phosphorylated histone H3 (pH3, red), and γH2AX (green) 24 h after infection. (Scale bars, 10 μm.) (E) Quantification of γH2AX foci in mitotic cells. Error bars represent SEs from three experiments.