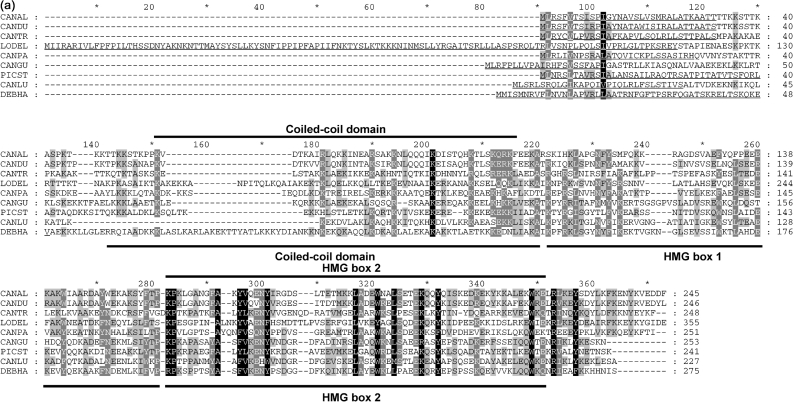
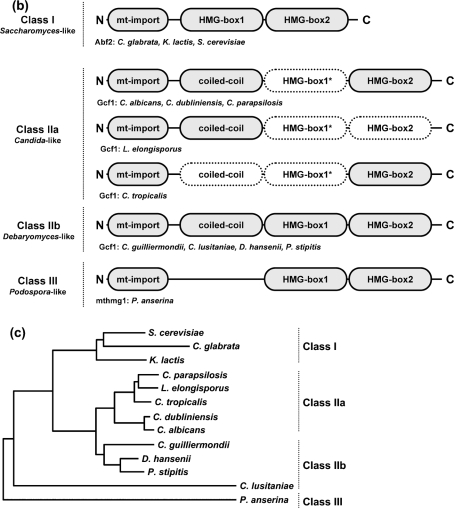
Fig. 1.
In silico analysis of mtHMGs. (a) Amino acid sequence alignment of yeast mtHMGs (class II members). The sequences were aligned using the AlignX utility of the Vector NTI 10.1.1 program package (Invitrogen) and the GeneDoc utility (Nicholas et al., 1997). CANAL, C. albicans; CANDU, C. dubliniensis; CANGU, C. guilliermondii; CANLU, C. lusitaniae; CANPA, C. parapsilosis; CANTR, C. tropicalis; DEBHA, D. hansenii; LODEL, L. elongisporus; PICST, P. stipitis. Positions of coiled-coil domain and HMG boxes in CaGcf1 (CANAL; subclass IIa) and DhGcf1 (DEBHA; subclass IIb) predicted by SMART are indicated above and below the alignment, respectively. Mitochondrial import presequences identified using MitoProtII are underlined. The probabilities of protein import into mitochondria were 0.9939 (CANAL), 0.9976 (CANDU), 0.9378 (CANGU), 0.8854 (CANLU), 0.9673 (CANPA), 0.6683 (CANTR), 0.9763 (DEBHA), 0.9986 (LODEL) and 0.9446 (PICST). (b) Modular structures of fungal mtHMGs. Domains predicted with low confidence are shown with dotted borders. The coiled-coil domain in the N-terminal region of CANAL, CANDU, CANGU, CANLU, CANPA, DEBHA, LODEL and PICST proteins was predicted by PCOILS with probabilities of 0.9–1.0 in at least two heptad repeat frames (i.e. 14, 21 and 28 amino acids). In the C. tropicalis homologue the predicted PCOILS probabilities were significantly lower (<0.6, 0.7 and 0.8 for frames 14, 21 and 28, respectively). The HMG boxes (Pfam and SMART accession numbers are PF00505 and SM00398, respectively) were predicted using SMART (normal mode) and InterProScan at default settings. The region corresponding to HMG box 1 is weakly conserved among the members of class II. This domain has not been detected by SMART and InterProScan in any of the subclass IIa proteins. Note that in the case of L. elongisporus the prediction of HMG box 2 was below the threshold, but its presence was inferred from the sequence homology. The three classes of fungal mtHMGs were defined using the protein length and the presence of protein domains. (c) Phylogenetic trees of fungal species with known mtDNA packaging proteins. The neighbour-joining tree was calculated from the D1/D2 sequences of the large subunit rRNA gene. The two groups within class II correspond to the split on the phylogenetic tree, which also supports the idea that subclass IIb architecture is ancestral to the subclass I and IIa proteins.