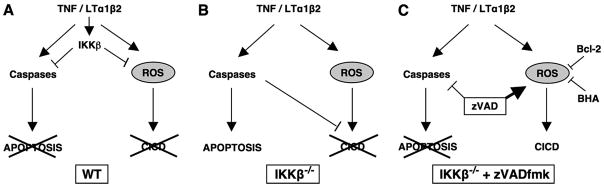
FIGURE 9. Model of apoptosis and CICD in WT and IKKβ−/− MEFs.
In this model activation is denoted by an arrowhead and inhibition by a straight line. A, in WT MEFs, TNF and LTα1β2 activate IKKβ that inhibits both caspase-dependent apoptosis and CICD. Caspases are blocked by the classical NF-κB-dependent induction of caspase inhibitors including c-FLIP and c-IAP2, and ROS are blocked by the up-regulation of antioxidant enzymes such as Mn-SOD (Fig. 8A). B, in the absence of IKKβ cytokines activate caspase-dependent apoptosis. ROS levels are increased possibly via a lack of induced Mn-SOD expression (Fig. 8A), and mitochondrial membrane potential is lost (Fig. 6A). However, in the presence of active caspases, CICD does not occur, and neither Bcl-2 (Figs. 6, C and D) nor BHA (Figs. 7, C and D) can block cell death. C, caspase-dependent apoptosis is blocked in IKKβ−/− MEFs stimulated with cytokines in the presence of zVADfmk. These cells die by CICD that can be inhibited by mitochondrial regulation via Bcl-2 overexpression (Figs. 6, C and D) or by ROS scavenging via BHA treatment (Figs. 7, C and D).