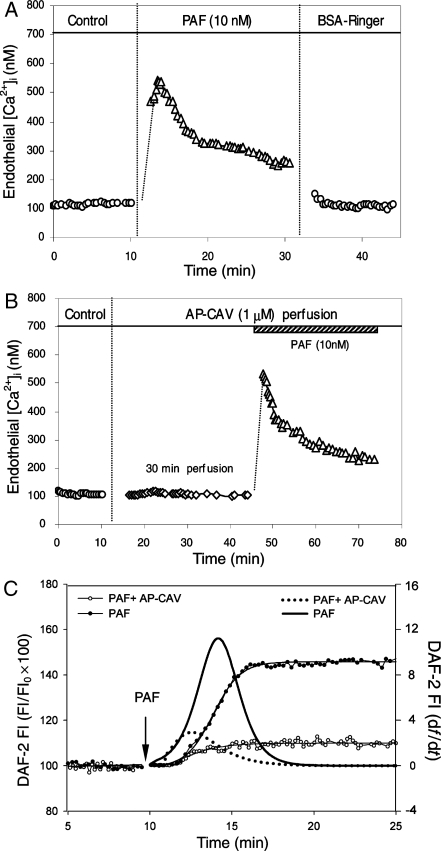
Figure 2.
AP-CAV attenuated PAF-induced NO production without affecting endothelial [Ca2+]i. (A) PAF-induced transient increases in endothelial [Ca2+]i in the absence of AP-CAV. (B) PAF induced a similar magnitude increase in endothelial [Ca2+]i in a AP-CAV pre-perfused vessel, indicating that AP-CAV has no effect on PAF-induced Ca2+ influx. (C) PAF-induced NO production in the presence or absence of AP-CAV in two of the experiments. PAF-induced cumulative DAF-2 FI, an indication of increased NO production, in the presence (open circle) or absence (filled circle) of AP-CAV is shown as a function of time (left y-axis). The differential conversion of the cumulative FI (df/dt, right y-axis) represents the NO production rate (solid line: PAF alone; dotted line: with AP-CAV perfusion).