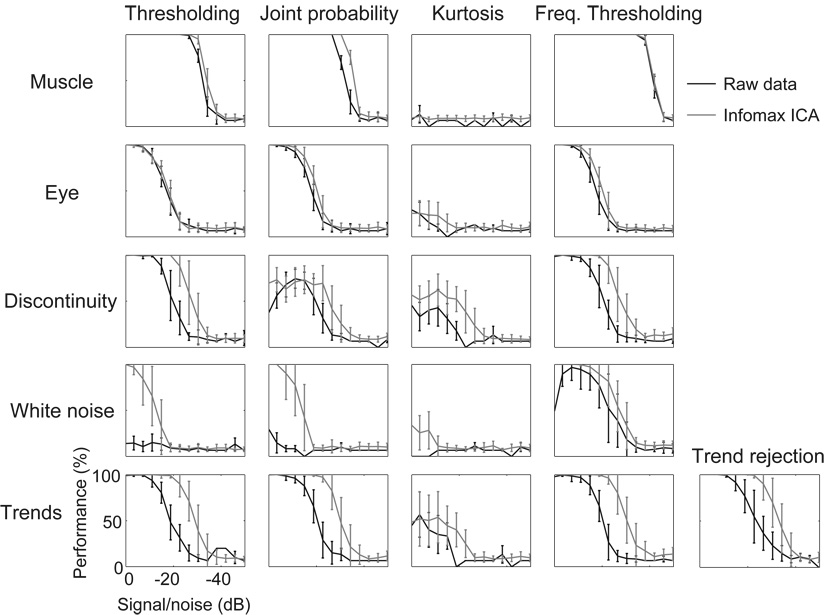
Figure 2.
Artifact detection performance (artifacts detected minus non-detected artifacts, divided by the total number of artifacts) by five methods (columns) applied to detection of the five types of simulated artifacts (rows, cf. Fig. 1) at a range of amplitudes (0 to −50 dB relative to the EEG). Linear trend detection (far right) was only used to detect trend artifacts. (Black traces): The five methods were first applied optimally to the best single-channel data for each artifact type. (Grey traces): The same methods were then applied to the best single independent components computed from the data by infomax ICA. Vertical error bars show ± 1 standard deviation in performance across 20 replications. Overall, for artifacts less than 40 dB below the EEG in strength spectral thresholding methods (right) performed best, and all detection methods performed better when applied to the independent component data.