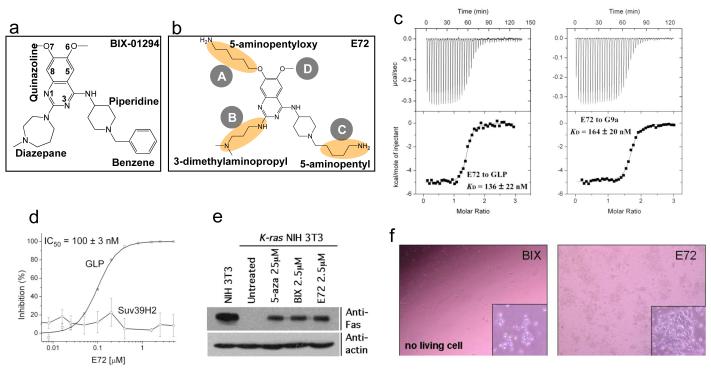
Figure 1.
Chemical structures for (a) BIX-01294, (b) E72, highlighted with changes. (c) The binding (KD values) of E72 compound to GLP (left panel) and G9a (right panel) are measured by isothermal titration calorimetry with a VP-ITC instrument (MicroCal) at 25°C. The titrations were conducted in buffer containing 20 mM Tris pH 8.0, 150 mM NaCl, 1.3-1.45% DMSO and 50 μM AdoMet. The sample chamber and syringe were filled with 20-30 μM GLP (or 21 μM G9a) and 260-350 μM (or 286 μM) compound, respectively. The data were processed using Origin 7.0 software. (d) The inhibition (IC50 values) of E72 against GLP or Suv39H2 is plotted against various concentrations of compound, under the conditions of 0.075 μM GLP or Suv39H2, 10 μM H3 peptide (residues 1-15), 100 μM AdoMet in the buffer of 20 mM Tris pH 8.5, 5 mM dithiothreitol (DTT), and 2% DMSO. The reaction mixture was incubated for 5 min (GLP) or 15 min (Suv39H2) at 30 °C, and subjected to mass-spectrometry-based inhibition assay as described 4. (e) Ras-mediated epigenetic silencing of Fas is derepressed with E72, BIX and 5-aza treatments, as described 4. (f) Mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells (TT2) 18 were treated for 24 h with each compound at 10 μM concentration, BIX-01294 (left panel), E72 (right) (see also Supplementary Table 1 and Fig. 3b).