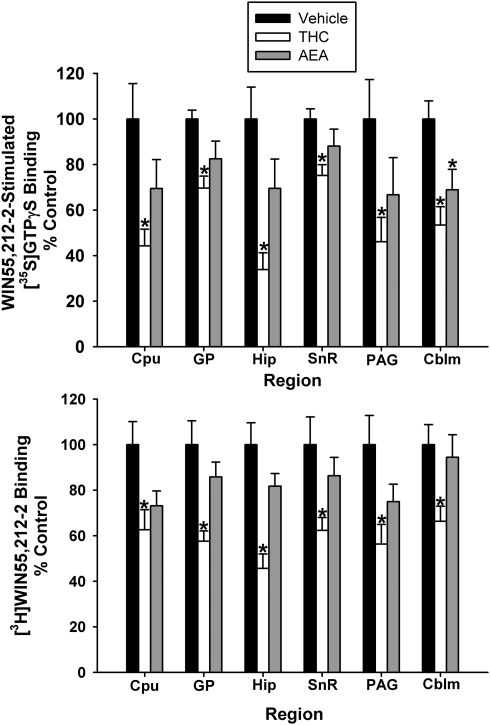
Figure 9.
Subchronic THC attenuates CB1 receptor binding and G-protein activity, whereas subchronic AEA produces minimal CB1 receptor adaptation. Net WIN55,212-2-stimulated [35S]GTPγS binding (top) and [3H]WIN55,212-2 binding (bottom) in THC- and AEA-treated FAAH−/− mice are expressed as a percentage of control (vehicle-treated) mice (n=8–12 mice/group, *p<0.05 different from vehicle-treated group by one-way ANOVA with a post hoc Dunnett's test).