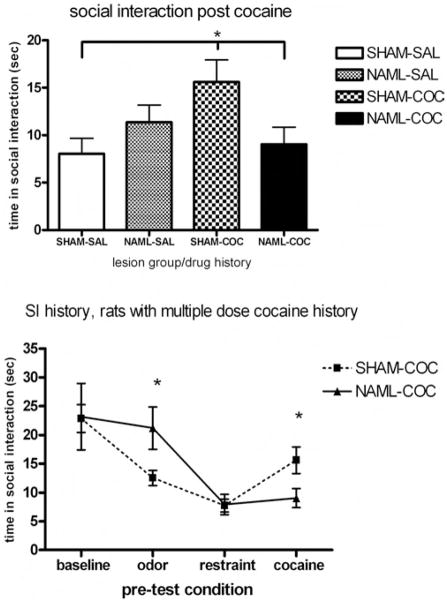
Figure 7.
Four days after the cocaine challenge, differential effects of repeated-cocaine- versus saline-dosing history emerged in social interaction (SI) among rats depending on lesion status (upper panel; analysis of variance [ANOVA] interaction between drug history and lesion, p < .05). Sham-operated (SHAM) rats with histories of multiple cocaine doses (SHAM-COC, N = 13) showed greater SI times than did SHAM rats with only saline histories prior to cocaine challenge (SHAM-SAL, N = 11) and NAML rats with histories of multiple cocaine doses (NAML-COC, N = 10; p < .05, least significant difference post hoc testing). In rats with multiple-cocaine-dose histories (lower panel), SI was differentially influenced by lesion status and pre-condition (ANOVA interaction, p < .05), with SI of NAML rats differing from that of SHAM rats immediately after predator odor exposure and 4 days after cocaine injections (*p < .05, post hoc t testing). Error bars represent ±1 SEM.