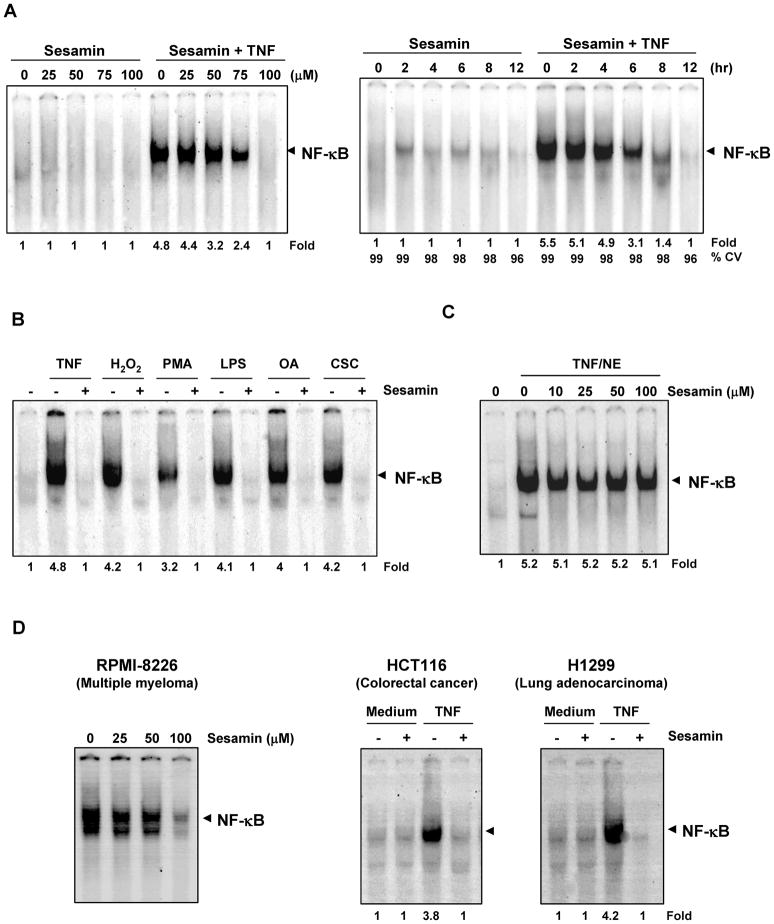
FIGURE 3.
(A) Dose- and time-dependent effect of sesamin on TNF-induced NF-κB activation. (Left) KBM-5 cells were incubated with the indicated concentrations of sesamin for 12 h and treated with 0.1 nM TNF for 30 min. (Right) KBM-5 cells were pre-incubated with 100 μM sesamin for the indicated time points and then treated with 0.1 nM TNF for 30 min. The nuclear extracts were assayed for NF-κB activation by EMSA. (B) Sesamin inhibits NF-κB activation induced by CSC, H2O2, PMA, LPS, okadaic acid and TNF. KBM-5 cells were preincubated with 100 μM sesamin for 12 h and then treated with 0.1 nM TNF for 30 min, 250 μM H2O2 for 2 hr, 25 ng/mL PMA for 2 hr, 10 μg/mL LPS for 1 hr, 500 nM okadaic acid for 4 hr, and 10 μg/mL CSC for 2 hr. Nuclear extracts were analyzed for NF-κB activation by EMSA. (C) Sesamin did not inhibit direct binding of NF-κB to DNA. Nuclear extracts were prepared from untreated KBM-5 cells or cells treated with 0.1 nM TNF for 30 min, incubated for 30 min with indicated concentrations of sesamin for 30 min and EMSA was performed. (D) Effect of sesamin on constitutive and inducible NF-κB activation. (Left) Human multiple myeloma cells (RPMI-8226) were incubated with the indicated concentrations of sesamin for 12 hr, the nuclear extracts were prepared and analyzed for NF-κB activation by EMSA. (Right) Human colorectal cancer cells (HCT116) and human lung adenocarcinoma cells (H1299) were pretreated with 100 μM sesamin for 12 hr, treated with 0.1 nM TNF for 30 min, and then EMSA was performed.