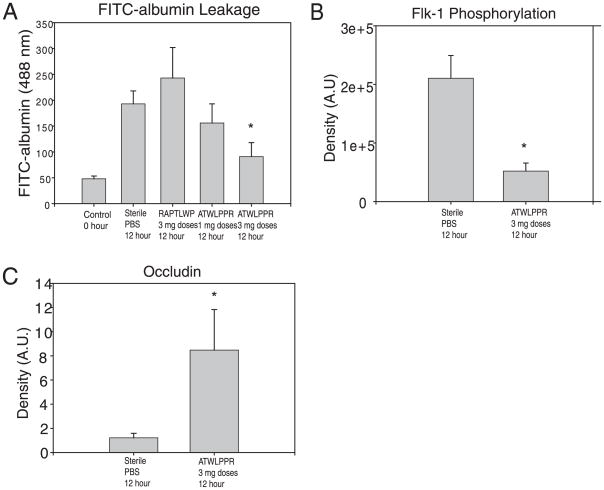
FIGURE 5.
Inhibition of VEGF coreceptor, NRP-1, reduces flk-1 phosphorylation and preserves BBB integrity. At 12 h postadministration of VP2121–130 to initiate CNS vascular permeability, C57BL/6 mouse brains were assessed for i.v.-administered FITC-albumin leakage. Mice were treated to 1- or 3-mg dose regimens of NRP-1 inhibitor ATWLPPR, 3 mg doses of mock scrambled peptide RAPTLWP, or sterile PBS (n = 6 animals per treatment group). TMEV-infected mock control E7 peptide-injected animals served as an additional negative control. A, Treatment with 3 mg doses of ATWLPPR resulted in significantly less FITC-albumin leakage into the CNS when compared to treatment with RAPTLWP or PBS-administered controls. Treatment with 3 mg doses of ATWLPPR (n = 9 mice) resulted in a significant decrease in (B) phosphorylation of flk-1 and preservation of (C) CEC BBB tight junction protein occludin levels when compared with PBS-treated animals (n = 6 mice). *Denotes statistical significance with p < 0.05 when compared with sterile PBS group.