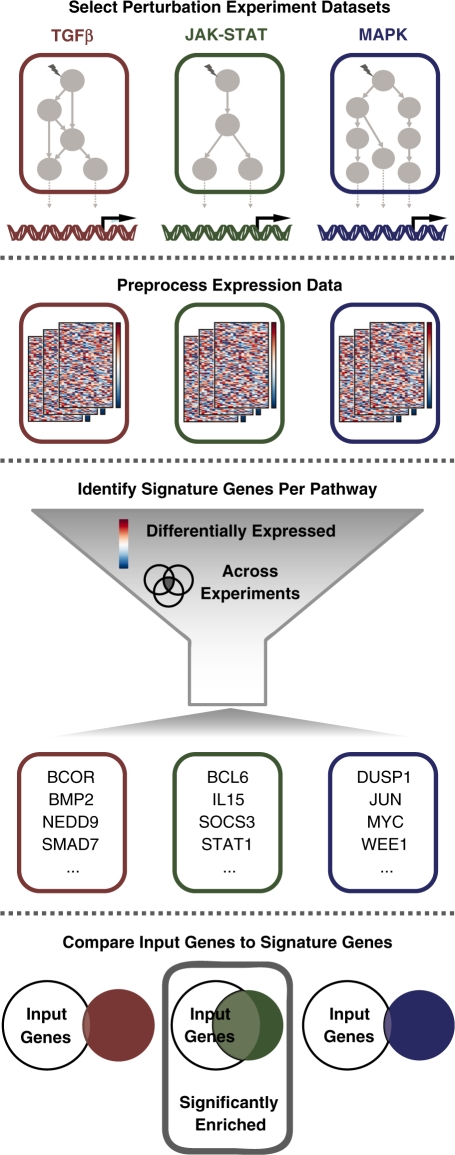
Figure 1.
Overview of the SPEED algorithm. The SPEED algorithm is based on the identification of signature genes that are consistently regulated by specific signaling pathways using publicly available micro-array data. Gene-expression data sets from single-pathway perturbation experiments were manually selected from the GEO database. Next, gene-expression values from the selected database were automatically processed using custom R-scripts, and expression changes were stored as Z-score rank percentiles in the SPEED database. The SPEED web server extracts signature genes per pathway on the fly based on user-specified parameters describing the level of differential expression (Z-score percentile; ex: top 1%) and the level of consistency across experiments (percentage of experimental data sets where a gene is differentially expressed; ex: at least 20%). Users can compare their own gene sets against the extracted signature genes to identify modulated upstream signaling pathways.