Figure 7.
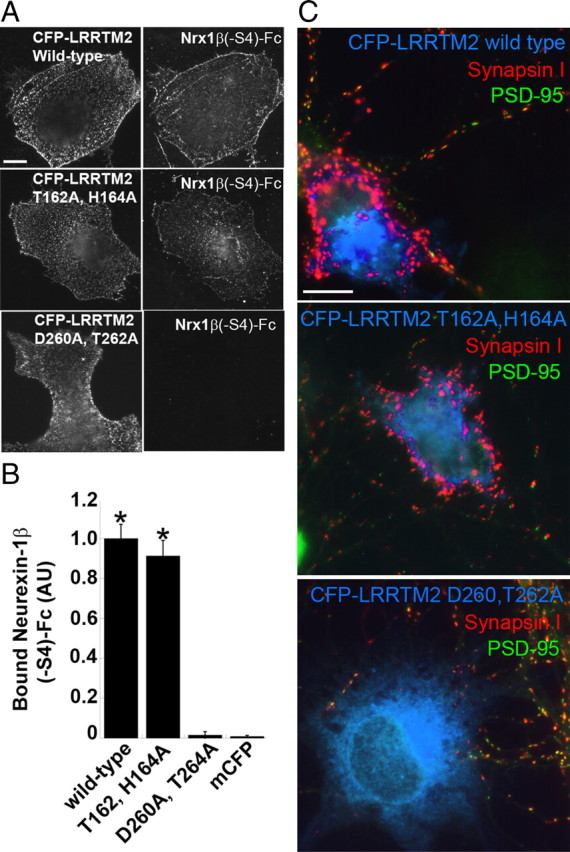
Mutation in LRRTM2 that prevents binding to neurexin abolishes its synaptogenic activity. A, Wild-type and point-mutation variants of LRRTM2 tagged at the N terminus with CFP to detect surface expression were expressed in COS7 cells and incubated with Nrx1β(−S4)-Fc. Nrx1β(−S4)-Fc had the same binding affinity to CFP-LRRTM2 T162A,H164A as to wild-type CFP-LRRTM2. However, Nrx1β(−S4)-Fc binding to D260A,T262A was abolished. B, Quantitation of the data in A [ANOVA, p < 0.0001; Tukey's post hoc test, *p < 0.001 compared to mCFP, (membrane associated CFP) n = 20]. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM. C, Coculture hemisynapse formation assay. COS7 cells expressing CFP-LRRTM2 wild-type and point-mutation variants were cocultured with hippocampal neurons. Wild-type CFP-LRRTM2 and CFP-LRRTM2 T162A,H164A induced clusters of synapsin I devoid of PSD-95 in contacting axons. CFP-LRRTM2 D260A,T262A expressing COS7 cells did not cluster synapsin I at axon contacts. Scale bars: 10 μm.
