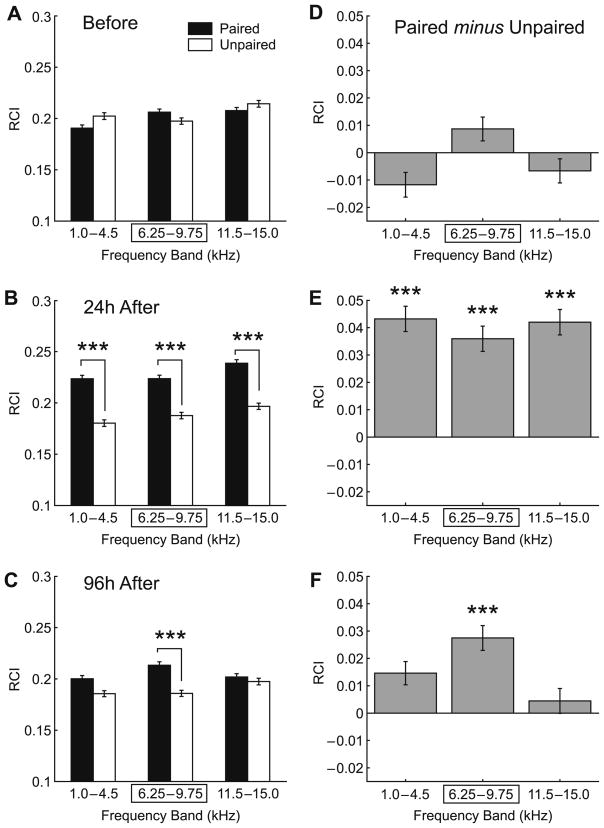
Fig. 5.
Effect of training and retention interval on NB-induced memory. Graph bars show mean ± SE of Respiration Change Index, RCI (Y-axis). (A) Pre-training (‘Before”) frequency generalization gradients to tones in three frequency bands: “Low” (1.0–4.5 kHz), “CS” (6.25–9.75 kHz [framed with rectangle]; the CS was 8.00 kHz) and “High” (11.5–15.0 kHz). There were no significant differences between Paired (black bars) and Unpaired (white bars) groups before training. (B) Post-training BFGGs at 24 h for the Paired and Unpaired groups. Note the significant difference in response in the all frequency bands between the groups indicating associative learning, which was not frequency-specific. (C) Post-training BFGGs at 96 h, for the Paired and Unpaired groups. Note the CS-specificity, due to decreased responses at the low and high-frequency bands, which rendered them no different from the Unpaired group. (D) Baseline between-group BFGG differences (“Paired minus Unpaired”). Note that the Paired group had slightly larger responsiveness to tones within the CS frequency band while the Unpaired group had slightly greater responses to tones within lower and higher frequency bands. There were no significant difference between groups at any frequency band (ANOVA: p > .20, see Section 3 for details). (E) Post-training (24 h) between-group differences. The Paired group had larger responsiveness to tones within each tested frequency band, including the CS-band compared to the Unpaired group. The response differences were significant for the entire distribution (ANOVA: p < .0001), that was attributable to the differences found within each tested frequency band (p < .0001, see Section 3 for details) as measured post hoc. (F) Post-training (96 h) between-group differences. The Paired group had larger responses to tones within each tested frequency band, including the CS-band compared to the Unpaired group. The response differences were significant for the entire distribution (ANOVA: p < .0001). However, in contrast to 24 h post-training the 96 h post-training between-group differences were attributable exclusively to the differences found within the CS frequency band (p < .0001, see Section 3 for details) as measured post hoc. Level of statistical significance: ***p < .005, Tukey’s test.