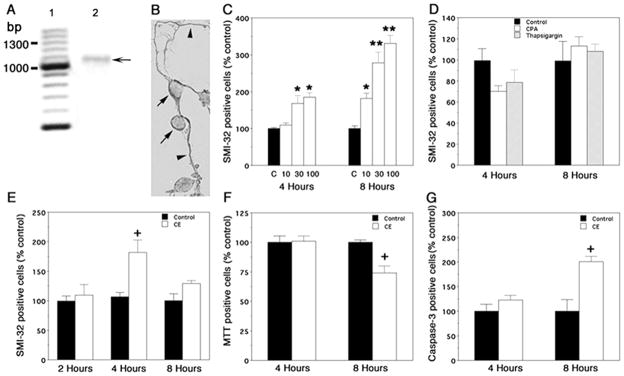
Figure 1. Effects of PMCA and SERCA inhibitors on spinal cord neurons, in vitro.
A) RT-PCR showing expression of PMCA2 in neuronal cultures. Lane 1: molecular weight marker; bp, base pairs; lane 2: RT-PCR product (arrow) at the predicted molecular weight (1014 bp). The identity of the band was further verified by sequence analysis. B) PMCA2 immunoreactivity in spinal cord neurons. Arrows and arrowheads point at immunopositive cells and processes, respectively. C) SMI-32 positive cell number after exposure of cultures to 10, 30, and 100 μM Na3VO4. C: control. D) Effects of SERCA inhibitors on SMI-32 positive cell number. CPA: cyclopiazonic acid. E) SMI-32 positive cells after exposure of cultures to 5 μM 5-(and-6)-carboxyeosin diacetate, succinimidyl ester (CE). F) Effects of CE on cell survival. G) Induction of activated caspase-3 in cells treated with CE. The experiments were repeated at least twice and yielded similar results. Values are presented as means ± SEM. Significantly different from controls *P < 0.003, **P< 0.0001 by ANOVA; +, significantly different from control by Student’s t test, P < 0.02; n = 6–12.