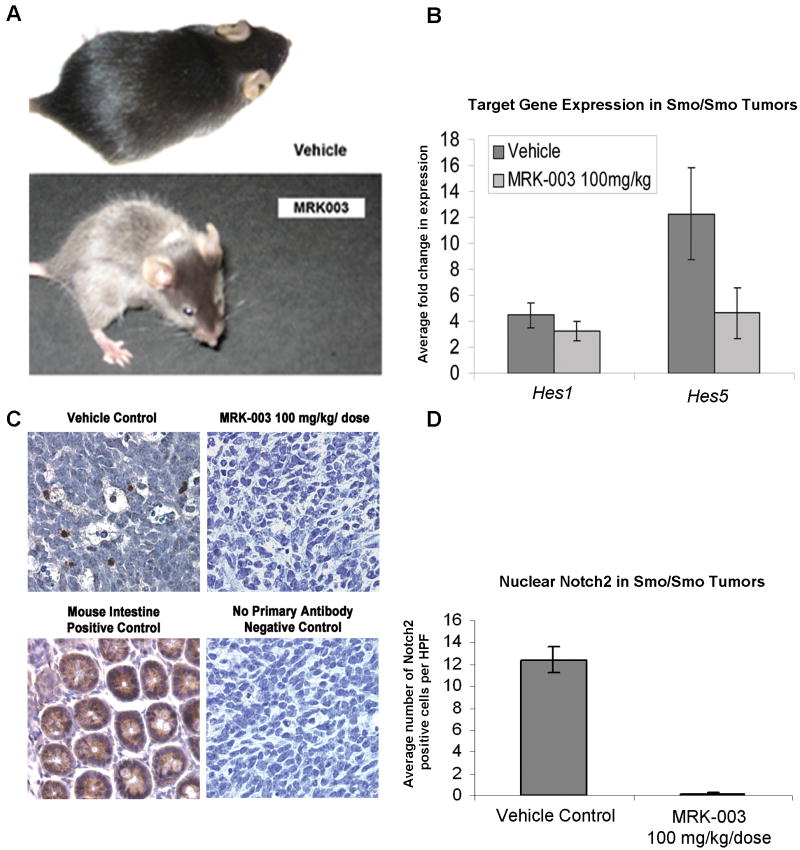
Figure 3. Analysis of MRK-003 on-target effects.
(3a) Smo/Smo mice maintained on a C57Bl/6 background that received 100 mg/kg/dose of MRK-003 by oral gavage developed gray hair and striped whiskers, while mice treated with enteral vehicle remained black. Hair graying is a phenotype caused by notch inhibition (Schouwey and Beermann, 2008). (3b) The canonical notch target gene Hes5 was downregulated by MRK-003 in Smo/Smo cerebellar tumors. Total RNA was extracted from cells using the Qiagen RNeasy Plus Kit and converted to cDNA using the ABI Taqman Reverse Transcription kit (Applied Biosystems (ABI)). Quantitative Real Time PCR was set up using ABI Taqman Master Mix and run on the Applied Biosystems 7900HT Real-Time PCR (384-well qPCR) System. Taqman primers (ABI) for mouse Hes1, Hes5 and Gapdh controls were used. Data was analyzed using SDS 2.3 software (ABI). All conditions were run in triplicate and normalized to mouse Gapdh controls. Expression of both MRK-003 treated (n=4) and vehicle control (n=8) samples were normalized to wild-type cerebella (n=3). Error bars represent average +/- SEM and p values were generated using a t-test. (3c) Notch2 immunohistochemistry demonstrates abundant Notch2 protein in vehicle-treated Smo/Smo medulloblastomas and in mouse intestine positive control, diminished Notch2 in MRK-003 treated Smo/Smo mice, and no staining in a negative control that lacked treatment with primary antibody. (3d) Cerebellar tumor sections were stained with an antibody recognizing Notch2 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) and five high power fields (HPF) were scored for each sample. Bars represent the average number of Notch2 positive cells per HPF, and error bars represent the standard error. A two-tailed t-test was used to determine p values.