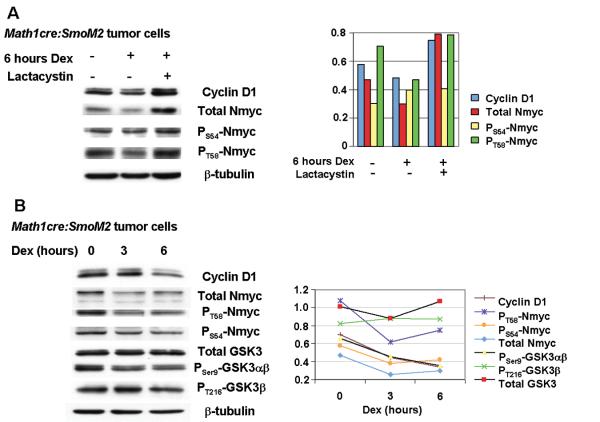
Figure 3.
Dexamethasone treatment of medulloblastoma cells results in proteasome-mediated destabilization of Nmyc and enhanced GSK3ß activity. (A) Dexamethasone treatment reduced levels of Nmyc in Math1-cre:SmoM2 medulloblastoma cells in vitro. Addition of the proteasome inhibitor, lactacystin, resulted in accumulation of total N-myc. PT58Nmyc levels -but not PS54Nmyc levels - were increased after dexamethasone treatment relative to β-tubulin loading controls. Histograms on the right delineate densitometric quantification. (B) Reduced Cyclin D1 and total Nmyc levels were detected after 3 and 6 hours of dexamethasone treatment. Levels of phosphorylated Nmyc were decreased, suggesting rapid Nmyc turnover after dexamethasone treatment. Consistent with this, levels of PSer9GSK3ß are decreased, suggesting increased activity of GSK3ß within this time course. Densitometric quantification is given on the right.