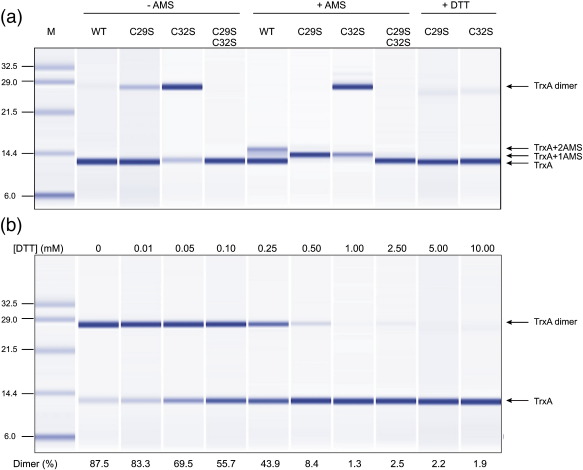
Fig. 2.
Redox states of BsTrxA monomers and dimers. (a) Purified His6-tagged BsTrxA proteins were separated by capillary electrophoresis using a 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent Technologies). WT, BsTrxA with wild-type active site; C29S, C29S single-mutant BsTrxA; C32S, C32S single-mutant BsTrxA; C29S–C32S, C29S–C32S double-mutant BsTrxA. To monitor the presence of free thiols in the purified BsTrxA proteins, samples were incubated in the presence or in the absence of 0.3 mM AMS (lanes marked + AMS or − AMS). To test whether the C29S and C32S dimers are formed by disulfide bonding, these proteins were incubated with 10 mM DTT (lanes marked + DTT). DTT was absent from all other samples. The image of the Bioanalyzer chromatogram was generated using the 2100 Expert Software package (Agilent Technologies). (b) C32S BsTrxA protein (∼ 2.5 μg) was reduced with increasing concentrations of DTT (shown on top of the panel) and separated by capillary electrophoresis as described for (a). The dimer-to-monomer ratios (Dimer [%]) are shown at the bottom of the panel.