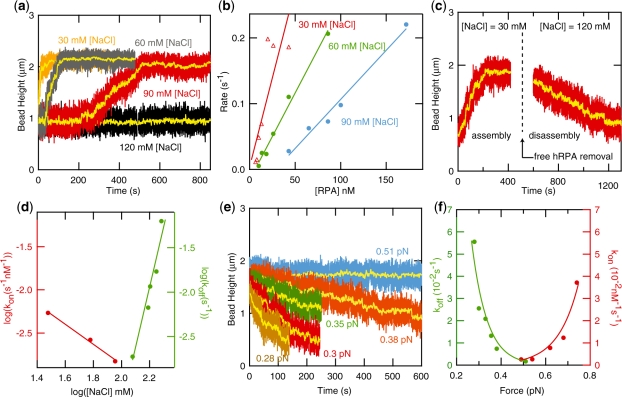
Figure 3.
Influence of helix (de-)stabilizing effects: salt and force. (a) Binding curves recorded at 0.5 pN and [RPA]=40 nM for [NaCl]=30, 60, 90 and 120 mM. The salt concentration has a marked effect on the binding kinetics. High-salt traces are characterized by a salt-dependent lag time and slower extension rates. (b) Extension rates at varying [hRPA] concentrations. The reaction rates are linearly dependent on [hRPA]. (c) Binding curve at low salt ([NaCl]=30 mM) followed by dissociation at high salt ([NaCl]=120 mM) after removal of hRPA. (d) Association and dissociation rates on a log–log scale. (e) Dissociation curves measured at varying stretching force. (f) Association and dissociation rates as function of force reveal a strong force dependence of the reaction kinetics.