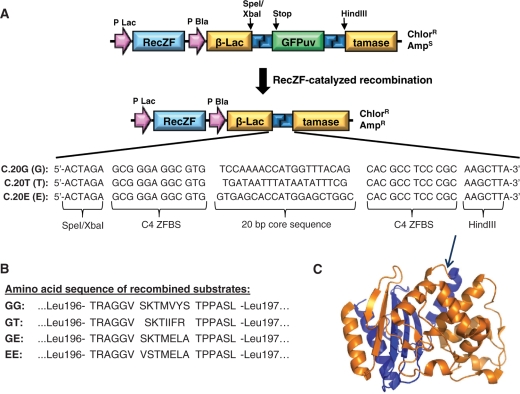
Figure 1.
Recombinase-dependent split gene reassembly system. (A) Structure of evolution vector before and after recombinase-mediated excision of the GFPuv fragment, with recombination target sites shown in blue. SpeI and HindIII restriction sites were inserted into the β-lactamase gene between Leu196 and Leu197 for convenient insertion of a GFPuv transgene flanked by recombination sites. The structure of a RecZF target site consists of a 20 bp core sequence flanked by zinc finger-binding sites (ZFBS). The C4 ZFBS was used in all plasmids and has been described previously (14). The sequences of various 20-bp core sequences used in this study are shown, including sequences derived from the natural Gin invertase and Tn3 resolvase target sites (20G and 20T, respectively), and a 20-bp sequence derived from the promoter of ErbB2 on human chromosome 17 (20E). (B) The predicted sequences of the 19-amino acid peptide that is grafted into the reassembled β-lactamase protein after excision of GFPuv are shown for the four evolution vectors used in this study. (C) Structure of TEM-1 β-lactamase. The N-terminal fragment is shown in orange, and the C-terminal fragment is shown in blue. The arrow indicates the insertion site of the peptide encoded by the recombination site, between Leu 196 and Leu 197 in the loop connecting helices 9 and 10.