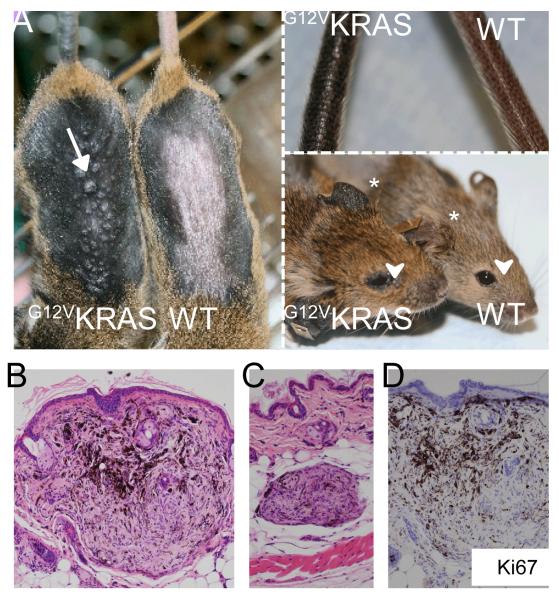
Figure 1. G12VKRAS induces benign melanocytic lesions in mice.
A. Left panel: Photograph showing hyper-pigmentation and small dome-shaped lesions (arrow) on the skin of TM-treated G12VKRAS;Tyr::CreERT2 (left) and control (right) mice. The fur was removed to reveal the skin. Upper right panel: photograph showing tail pigmentation on a TM-treated G12VKRAS;Tyr::CreERT2 (left) and control (right) mouse. Lower right panel: photograph showing ear pigmentation (*) and peri-orbital areas (arrowhead) of a TM-treated G12VKRAS;Tyr::CreERT2 (left) and control (right) mouse.
B. Photomicrograph of a haematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained paraffin section of a nevus near the epidermal-dermal junction. Note the pushing borders of the lesion.
C. Photomicrograph of an H&E-stained paraffin section of a nevus found within the dermo-hypodermal interface of a TM-treated G12VKRAS;Tyr::CreERT2 mouse.
D. Photomicrograph showing lack of Ki67 expression in a nevus from a TM-treated G12VKRAS;Tyr::CreERT2 mouse. The section is counterstained with haematoxylin (purple) and the nevus is devoid of mitotic figures.