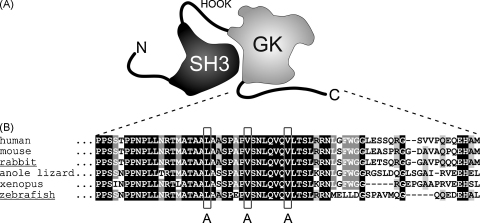
Fig. 1.
A conserved leucine-valine heptad repeat motif in the DHPRβ1a C-terminus. (A) Cartoon of the domain organization of the β1a subunit based on crystal structure models [28–30]. (B) Sequence alignment of β1a C-termini from different vertebrate classes, from fish to human, showed the conservation of the β1a-specific leucine-valine heptad repeat motif (boxed). To test for the contribution of the heptad repeat motif in skeletal muscle EC coupling, the LVV residues (boxed) were substituted by AAA (β1aAAA) in zebrafish and rabbit β1a subunits to be expressed in the zebrafish β1-null mutant relaxed system. Sequence for human (Homo sapiens) β1a, anole lizard (Anolis carolinensis) β1a, and Xenopus (Xenopus tropicalis) β1a were extracted from genomic assemblies at http://www.ensembl.org using a BLAST search with zf-β1a or rb-β1a cDNA sequences. GeneBank accession numbers for all other sequences used are: mouse (Mus musculus) β1a, NM_031173; rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) β1a, NM_001082279 and zebrafish (Danio rerio) β1a, AY952462.