Figure 1.
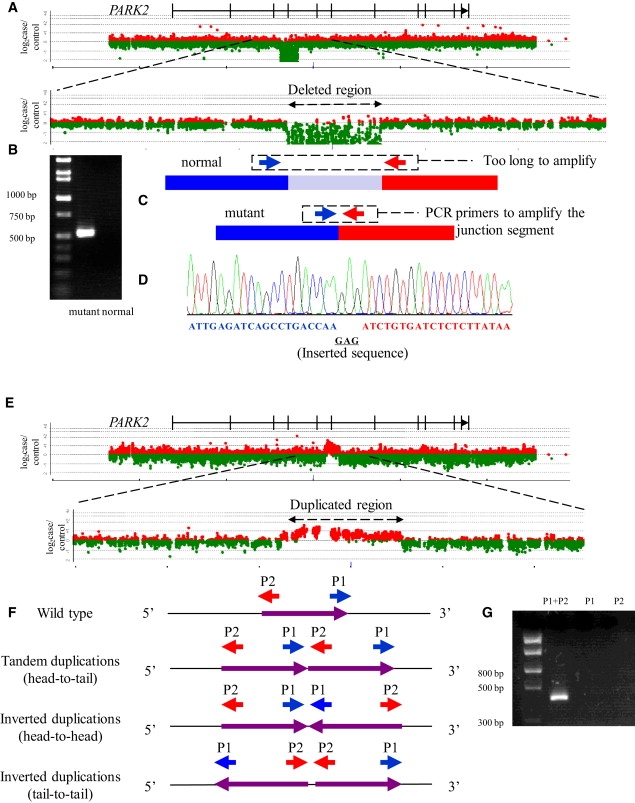
Determination of Breakpoint-Junction Sequences in PARK2 by Custom-Designed High-Density Array CGH Analysis
(A) Scan data of array CGH analysis of a patient with AR-JP with 82 kb homozygous deletions (exon 4 of PARK2). The horizontal axis represents the nucleotide position. The vertical axis represents log2 (ratio of case to reference signal intensities on array CGH). Dots of log2 (ratio of case to reference signal intensities) larger than 0 are shown in red, and those smaller than 0 are shown in green. The physical map of PARK2 is also shown above the scan data.
(B) Agarose gel electrophoresis of PCR products derived from the patient's genomic DNA obtained by employing primer pairs flanking the deletion. Amplifications did not occur in normal alleles because the segment between primers was too large (82 kb), while the band corresponding to the PCR products of 520 bp derived from the deletion allele was clearly visualized.
(C) Design of primer pairs for specific amplification of the deletion allele by PCR. A pair of oligonucleotide primers (denoted by red and blue arrows) was designed to amplify the segment across the breakpoint junction.
(D) Electropherogram of amplified segment encompassing breakpoint junctions. The nucleotide sequence corresponding to the segment upstream of the deletion is shown in blue, and the sequence corresponding to the segment downstream of the deletion is shown in red. The underlined inserted sequence not identical to either the upstream or the downstream segment is shown in black.
(E) Scan data of array CGH analysis of a patient with AR-JP with a homozygous duplication (exons 6 of PARK2) that turned out to be a tandem duplication. The horizontal axis represents the nucleotide position. The vertical axis represents log2 (ratio of case to reference signal intensities on array CGH). Dots of log2 (ratio of case to reference signal intensities) larger than 0 are shown in red, and those smaller than 0 are shown in green.
(F) Design of primer pairs for specific amplification of the duplicated allele by PCR based on head-to-tail, head-to-head, and tail-to-tail models. Oligonucleotide primers are denoted by red and blue arrows.
(G) Agarose gel electrophoresis of the PCR products derived from patient's genomic DNA obtained by employing primer pairs flanking duplicated segment. The PCR products are generated only when appropriate primers are used for amplification of rearranged genomic DNA segments.
