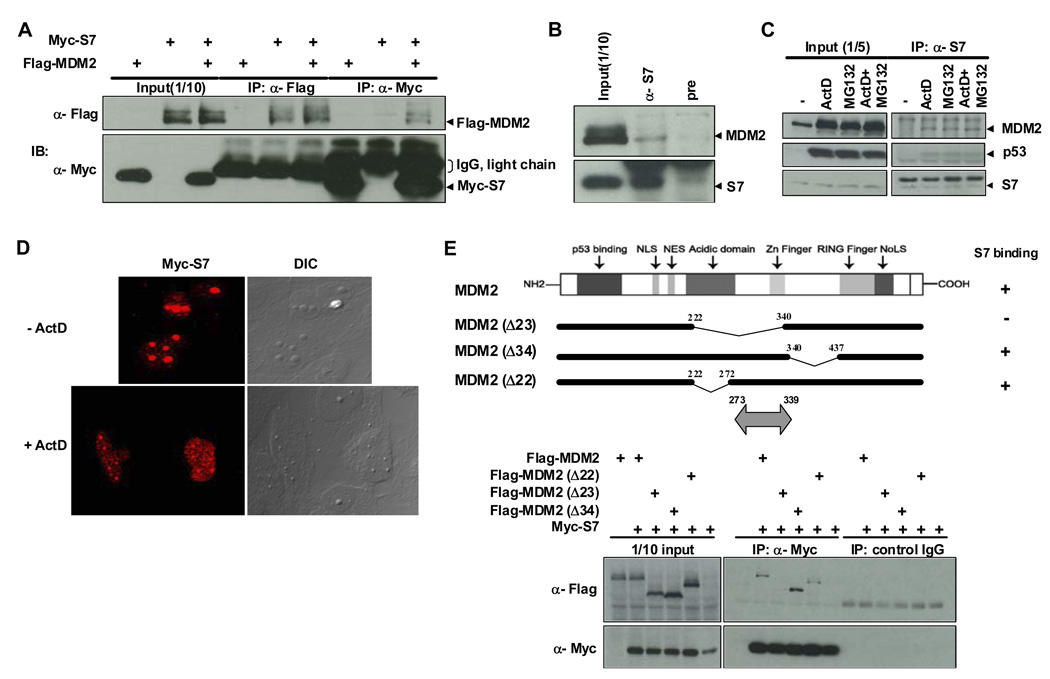
Figure 1. Binding between MDM2 and Ribosomal Protein S7 and Mapping of the MDM2 Domain for S7 Binding.
(A) Interaction between ectopic MDM2 and S7. H1299 cells were transfected with plasmids expressing Flag-MDM2 (1.5 µg), Myc-S7 (1.5 µg), or both (1.5 µg each) as indicated. Twenty-four hours after transfection, whole-cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-Flag or anti-Myc antibodies followed by immunoblotting (IB) with indicated antibodies. IgG light chains cross-reacting with anti-Myc antibody are also indicated. (B) Co-association of endogenous MDM2 and S7. Whole-cell lysates prepared from HCT116 cells were subjected to IP with either anti-S7 or pre-immune serum, followed by IB with anti-MDM2 and anti-S7 antibodies. (C) Increased binding between endogenous MDM2 and S7 in response to ActD or MG132 treatment. HCT116 cells were treated with ActD (5 nM), MG132 (20 µM) or both for 6 hours before harvesting. IP and IB were carried out as in (B). (D) Relocalization of ectopic S7 in response to ActD treatment. U2OS cells were transfected with a Myc-S7 (1.5 µg). Twenty hours after transfection, the cells were treated with ActD (5 nM) for 7 hours, and then subjected to immunofluorescent staining. (E) Mapping of the MDM2 domain for S7 binding. H1299 cells were transfected with plasmids (1.5 µg each) expressing different MDM2 deletion mutants as indicated. IP with anti-Myc antibody or control mouse IgG was carried out as in (A) and followed by IB with indicated antibodies. Schematic representation of MDM2 mutants used for transfection is shown on top with the S7 binding region indicated as double headed arrow at bottom.