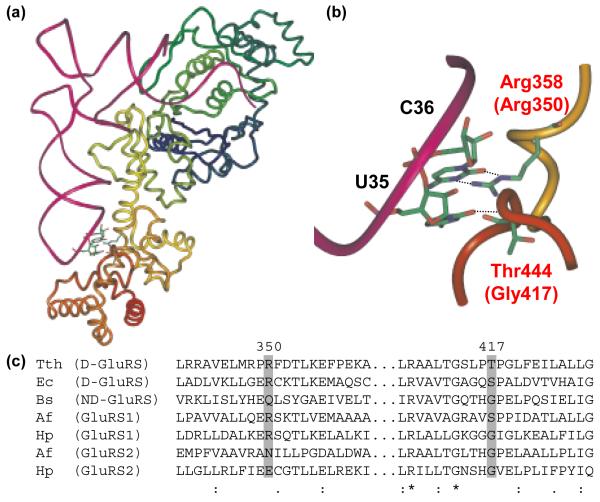
Figure 1.
Anticodon recognition and conservation in GluRS. (a) The crystal structure of TTh GluRS-D and tRNAGlu (Protein databank ID: 1G59).20 The tRNA is shown as a magenta tube and GluRS is shown in a multicolored ribbon format. Specific interactions between U35 and C36 in the tRNAGlu anticodon with the D-GluRS anticodon-binding domain are shown as ball and stick figures. (b) A close-up of the anticodon loop of tRNAGlu, complexed with Tth GluRS-D, showing the hydrogen bond interactions between Arg358 (Arg 350 in Hp GluRS1) and C36 and the backbone interaction between Thr444 (Gly417 in Hp GluRS2) and U35. Panels A and B were generated using Imol v. 0.30 (www.pirx.com). (c) Representative alignment of several known GluRS sequences, highlighting the distribution of Arg350 and Gly417 amongst the different GluRS categories (Arg350 and Gly417 represent the amino acids from Hp GluRS1 and GluRS2, respectively). The alignment was generated using ClustalX.21 All sequences were obtained from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov). Abbreviations: TTh - Thermus thermophilus; Ec - Escherichia coli; Bs - Bacillus subtilis; Af - Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans; Hp - H. pylori. GenBank accession nos. AAS80418 (Tth), AAA65715 (Ec), CAB11868 (Bs), AAD07544 (Hp1), AAD07704 (Hp2). Af GluRS1 and GluRS2 were identified by tBlastN analysis of the incomplete Af genome sequence using the Hp GluRS1 and GluRS2 sequences, respectively (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sutils/genom_table.cgi); the tRNA specificities of these two enzymes have been reported previously,9 however the genes are not yet annotated. Hp GluRS1, GluRS2, tRNAGlu1, tRNAGlu2 and tRNAGln were overexpressed or overtranscribed in and purified from E. coli, as described previously.8 Four mutant Hp GluRS variants (Arg350Glu GluRS1, Glu334Arg GluRS2, Gly417Thr GluRS2, and Glu334Arg/Gly417Thr GluRS2) were constructed for comparison to wild-type GluRS1 and GluRS2. These mutations were introduced into pSS001, pSS002 or pJHL003 using the QuikChange Site-Directed® Mutagenesis Kit (Stratagene). The Arg350Glu mutation was inserted into GluRS1 (pSS001) using the two complementary primers JHL#13 (5′-GACGCTCTCAAAGAAGAATCTCAAACAC-3′), and JHL#14 (5′-GTGTTTGAGATTCTTCTTTGAGAGCGTC-3′). Similarly, primer JHL#9 (5′-GCTTTTAAGATTGTTTATAGAAAGATGCGGTACCCTTTTAGAATTG-3′) and its complement JHL #10 (5′-ATTCTAAAAGGGTACCGCATCTTTCTATAAACAATCTTAAAAGC-3′) introduced the Glu334Arg mutation into pSS002, to generate pJHL003. JHL#42 (5′CCGGGAACTCGCATACCGTTGAATTGCC-3′) and JHL#43 (5′GGCAATTCAACGGTATGCGAGTTCCC-3′) were used to introduce the Gly417Thr mutation into pSS002, to generate pJHL019; these primers were also used to generate the double mutant Glu334Arg/Gly417Thr (pJHL020) from pJHL003. Overexpression and purification of each enzyme was accomplished by Ni-NTA affinity as described for GluRS1 and GluRS2.8