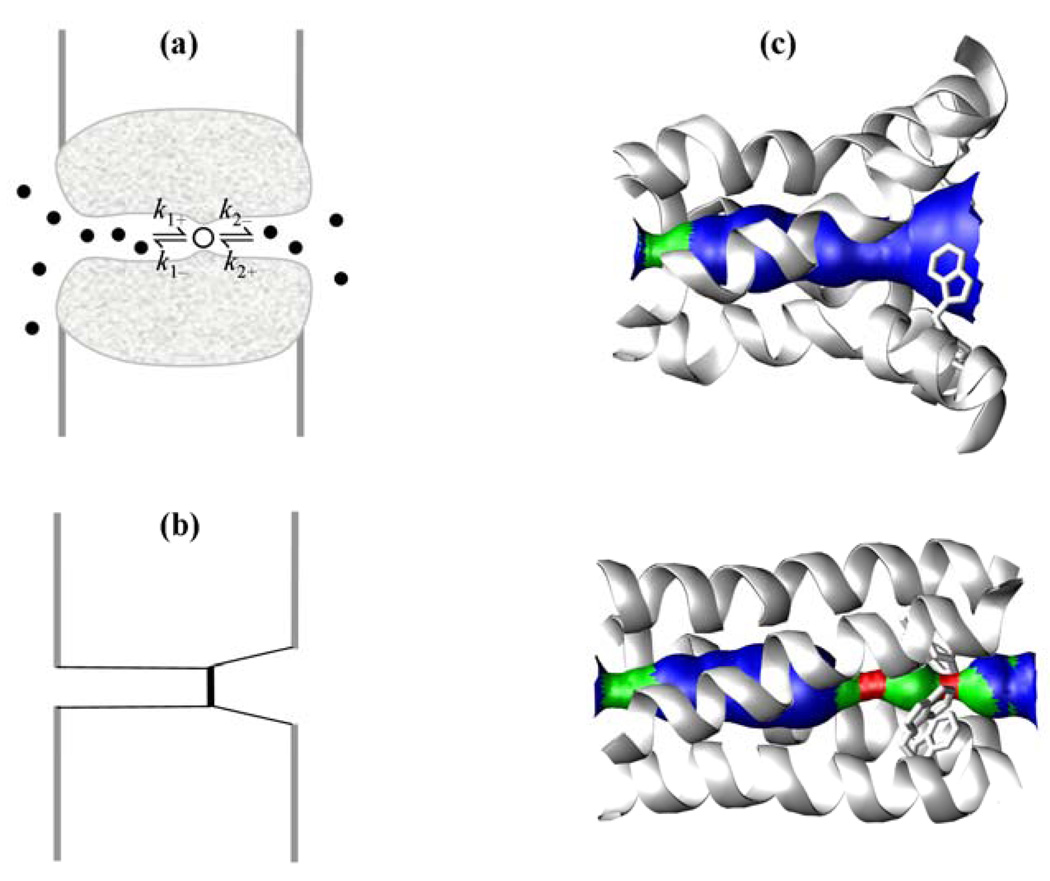
Figure 1.
A transmembrane ion channel with an internal binding site. (a) Diffusion of ions into the pore and binding at the internal site. (b) Idealized geometry of the pore. (c) Open and closed conformations of the M2 proton channel, which consists of four identical helical subunits. Top: open conformation in which proton binding from the C-terminal side (on the right) is allowed. Bottom: closed conformation in which proton binding from the C-terminal side is prohibited by the primary gate residue Trp41, which is shown as sticks. The constriction on the left comes from Val27; the constriction near the middle of the pore seen in the bottom panel comes from His37, which is the proton binding site. Part (c) is adapted from Yi et al.4 with permission; copyright (2009) the National Academy of Sciences, U.S.A.