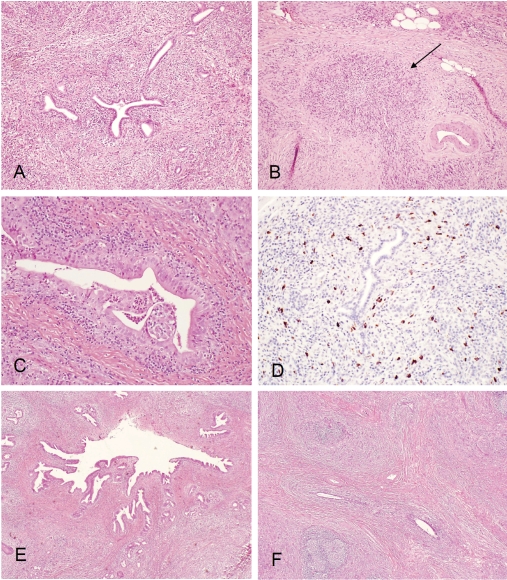
Figure 1.
(A), Type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis (lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing pancreatitis): low power view showing periductal lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate and storiform fibrosis with inflammatory cellular stroma. (B), Obliterative phlebitis (arrow): dense peri- and intra-venular inflammatory infiltrate with fibrosis destroying the endothelium and obliterating the lumen. (C), Granulocyte epithelial lesion (GEL) in type 2 autoimmune pancreatitis (idiopathic duct centric pancreatitis): periductal lymphoplasmacytic and neutrophilic infiltrate with intra-epithelium and intra-lumen neutro-philic infiltrate; destruction of small ducts and ductal epithelium, lobular lymphoplasmacytic and neutrophilic infiltrate. (D), IgG4 immunostain: markedly increased (>30/high power filed) periductal IgG4+ plasma cell infiltrate. (E), IgG4 associated cholangitis: low power view showing periductal lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate and storiform fibrosis. (F), Chronic sclerosingsialadenitis (Küttner tumor) showing dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate and storiform fibrosis destroying glandular structures.