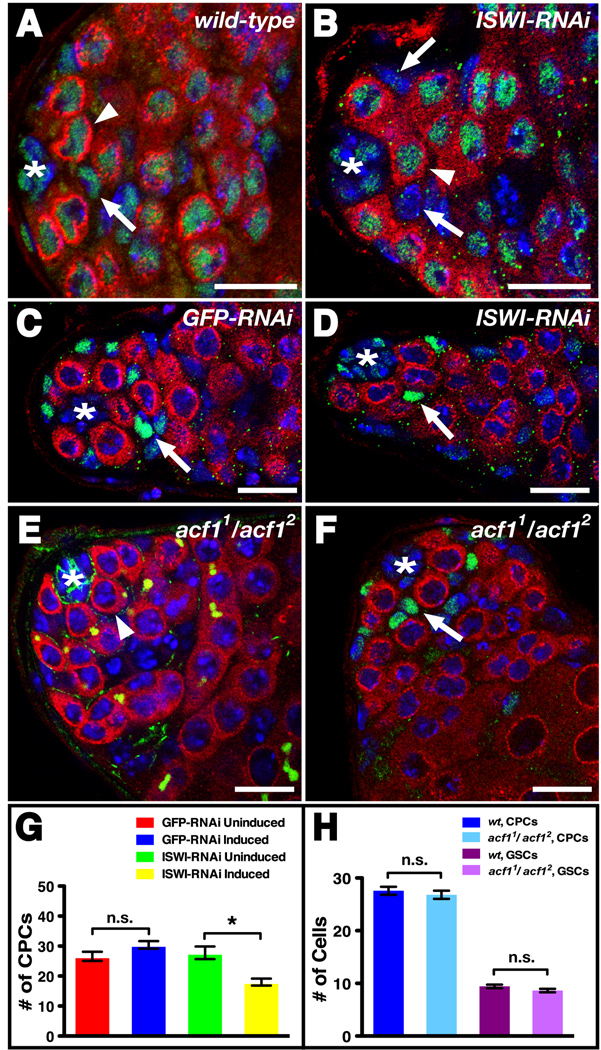
Figure 4. NURF is the sole ISWI-containing chromatin remodeling complex required for stem cell maintenance in the Drosophila testis.
(A–B) Testes immunostained with anti-ISWI (green), anti-Vasa (red), and DAPI (blue). An asterisk denotes the hub. (A) In wild-type testes, ISWI is expressed at comparable levels in CPCs (arrows) and GSCs (arrowhead). (B) ISWI-RNAi knockdown in CPCs and their daughters reduces ISWI expression in CPCs (arrows) compared to GSCs (arrowhead). (C–D) Testes immunostained with anti-Vasa (red), CPC marker anti-Zfh-1 (green), and DAPI (blue) expressing (C) GFP-RNAi or (D) ISWI-RNAi in CPCs (arrows) and their daughters. When compared to controls (C), a reduction in ISWI leads to fewer CPCs around the hub (*) (D). (E) acf1 homozygous mutant testis immunostained with anti-Vasa (red), anti-Armadillo (green), anti-1B1 (green), and DAPI (blue) containing a wild-type number of GSCs (one indicated, arrowhead) surrounding the hub (*). (F) acf1 homozygous mutant testis immunostained with anti-Vasa (red), anti-Zfh-1 (green), and DAPI (blue) containing a wild-type number of CPCs (one indicated, arrow) surrounding the hub (*). (G) ISWI-RNAi knockdown in CPCs and their daughters leads to a significant decrease in CPCs [n.s. (not significant), p-value > 0.05; *p-value < 0.001]. (H) acf1 homozygous mutant testes have the same number of GSCs and CPCs as wild-type (n.s., p-value > 0.05). Data are represented as mean +/− SEM. Bars, 10 microns.