Fig 1.
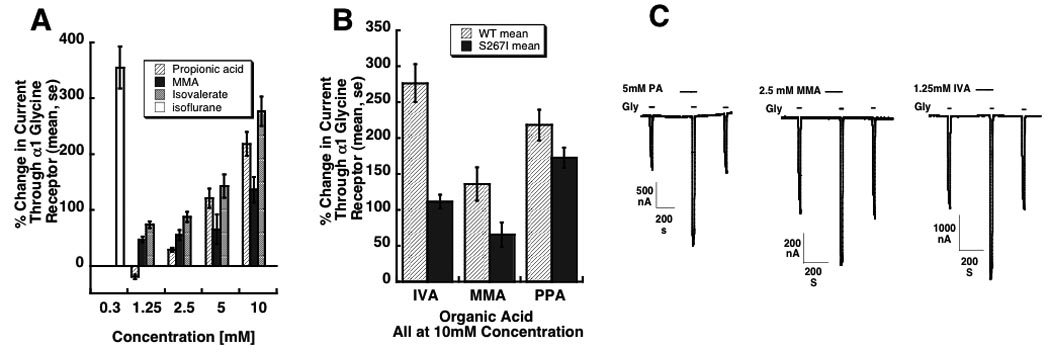
Modulation of α1 glycine receptor function by isovaleric acid, methylmalonic acid, and propionic acid. Panel A: 100 second exposures to propionic, methylmalonic (MMA), and isovaleric acid increases currents through homomeric α1 glycine receptors in response to EC5 glycine. Receptors were expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes and studied by two-electrode voltage clamping. Currents through glycine receptors increase in a concentration-dependent manner. The effect of 0.3mM isoflurane is shown for comparison. Panel B: Mutant S267I glycine receptors engineered to have a reduced modulatory response to isoflurane and ethanol also have a reduced response to isovaleric (IVA) and methylmalonic (MMA) acid (p < 0.05). The effect of propionic acid (PPA) is not statistically significant. Panel C: current tracings showing the effect of 5mM propionic acid (PA), 2.5 mM methylmalonic acid (MMA), and 1.25 mM isovaleric acid (IVA). Three peaks are shown for each acid: the first is in response to agonist (glycine) alone, the second to acid and agonist, and the third to agonist after washout of the acid.
