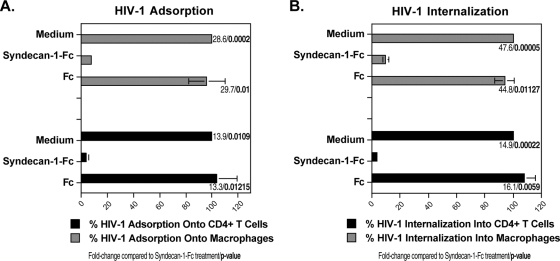
FIG. 3.
The syndecan-Fc hybrid molecule blocks HIV-1 infection by inhibiting viral entry. CD4+ T lymphocytes (500,000 cells) or macrophages (150,000 cells) were exposed to 5 ng of p24 of JR-CSF in the presence or absence of syndecan-1-Fc or control Fc (5 μg/ml). To measure virus adsorption (A), cells were exposed to virus for 2 h at 4°C, washed twice with PBS, and lysed (not trypsinized), and amounts of capsid in cell lysate were quantified by p24 ELISA. To measure virus internalization (B), plates containing cells and viruses were first centrifuged at 2,000 × g (spinoculation) for 3 h at 4°C. Cells were washed twice to remove unbound virus and then placed at 37°C for 4 h in the presence of Fc or syndecan-1-Fc (5 μg/ml). Cells were then trypsinized and lysed. Amounts of internalized virus were quantified by measuring amounts of capsid in cell lysates by p24 ELISA. Results are expressed as the percentage of internalization relative to maximal adsorption, and internalization in the absence of Fc proteins is arbitrarily fixed at 100. The points are median values (triplicate) and error bars represent standard errors of triplicates. The P values were calculated using a one-sided t test assuming equal variances.