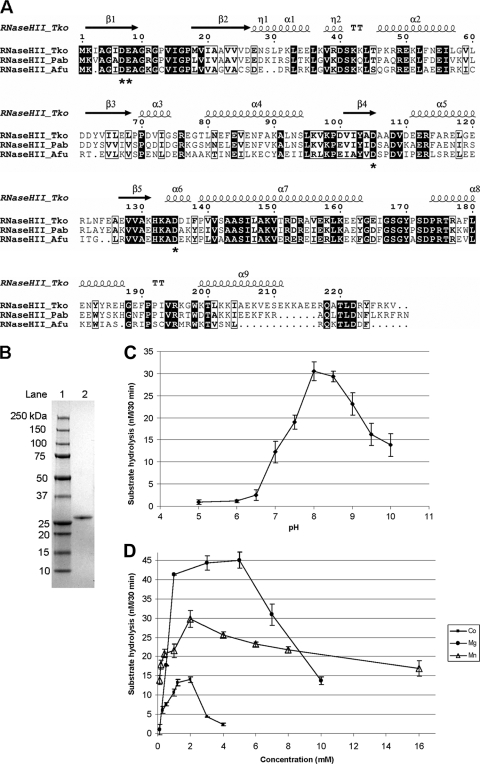
FIG. 1.
Enzymatic properties of PabRNase HII. (A) Alignment of the amino acid sequences of archaeal RNase HII homologues. Sequences are from the Euryarchaeota species P. abyssi (Pab; accession number gi 14520734), T. kodakaraensis (Tko; accession number gi 57640740), and A. fulgidus (Afu; accession number gi 11498229). Conserved amino acid residues are shaded in black. Similar amino acid residues are boxed. Proposed active-site residues are indicated by asterisks. Secondary structure is shown above the sequences, denoting β sheets (arrows) and α helices (ribbons). (B) Gradient (4 to 20%) SDS-PAGE of purified, recombinant, His6-tagged PabRNase HII (0.5 μg; lane 2) and molecular mass markers (lane 1) stained with Coomassie blue. (C) pH dependence. Enzymatic activities were determined at 60°C for 30 min in reaction buffer containing 50 mM Tris-HCl, 5 mM dithiothreitol, 5 mM MgCl2, 50 nM PabRNase HII, and 50 nM RNA-DNA/DNA substrate (S1) with pH values ranging from 5 to 10. Data are the averages of triplicate measurements. (D) Divalent cation dependence. Enzymatic activities were determined at 60°C for 30 min in reaction buffer containing 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8), 5 mM dithiothreitol, 50 nM PabRNase HII, and 50 nM RNA-DNA/DNA substrate (S1) at the indicated concentrations of MgCl2 (•), MnCl2 (▵), and CoCl2 (▪). Data are the averages of triplicate measurements.