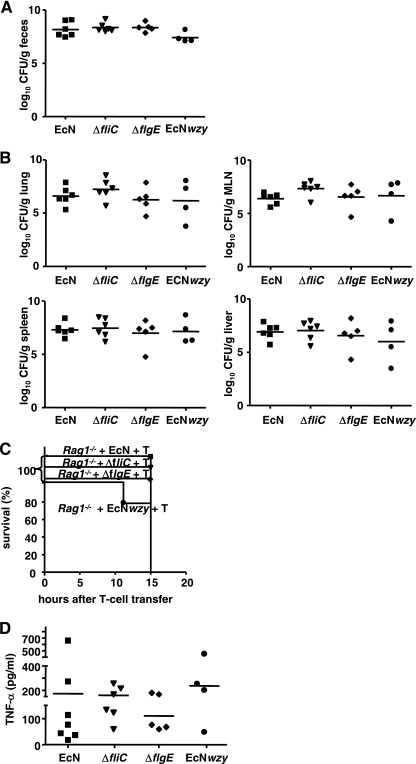
FIG. 4.
Translocation in germfree Rag1−/− mice is independent of LPS- or flagellum-mediated signals. Groups of at least five GF-raised Rag1−/− mice were challenged with 1 × 108 CFU of the ΔfliC mutant, the ΔflgE mutant, the E. coli strain Nissle 1917 wzy mutant (EcNwzy), or E. coli wild-type strain Nissle 1917 (EcN). Six days after challenge Rag1−/− mice were reconstituted with naïve T cells. (A) Numbers of CFU in feces at 1 day after transfer. Each symbol indicates the data for one animal. (B) Numbers of CFU in organs at 1 day after transfer. Each symbol indicates the data for one animal. (C) Kaplan-Meier survival curves for Rag1−/− mice challenged with either E. coli strain Nissle 1917 (▪), the ΔfliC mutant (▾), the ΔflgE mutant (⧫), or the E. coli strain Nissle 1917 wzy mutant (•) after T cell reconstitution. (D) TNF-α concentrations in sera of T-cell-reconstituted GF-raised Rag1−/− mice challenged with E. coli strain Nissle 1917, the ΔfliC mutant, the ΔflgE mutant, or the E. coli strain Nissle 1917 wzy mutant. TNF-α concentrations were determined by ELISA.