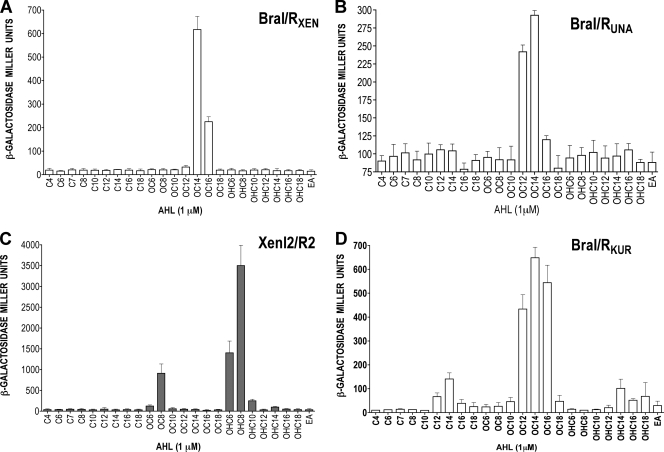
FIG. 3.
Determination of the biologically active AHL for BraRXEN, XenR2, BraRUNA, and BraRKUR AHL sensor/regulators. (A) Determination of the cognate AHL for the BraI/RXEN system of B. xenovorans. Bars correspond to β-galactosidase activities determined for E. coli harboring pQEXENR1 and pMPXENI1. (B) Determination of the cognate AHL for the BraI/RUNA system of B. unamae. Bars correspond to β-galactosidase activities determined for E. coli harboring pQEUNAR and pMPUNAI combination. (C) Determination of the cognate AHL for the XenI2/R2 system of B. xenovorans. Bars correspond to β-galactosidase activities determined for E. coli harboring pQEXENR2 and pMPX2I. (D) Determination of the cognate AHL for the BraI/RKUR system of B. kururiensis. Bars correspond to β-galactosidase activities determined for E. coli harboring pQEBRAR and PBRAI (73). Transcriptional fusions were harbored independently in E. coli expressing either BraRXEN or XenR2 proteins; various exogenous AHLs (1 μM) were provided as indicated, and the β-galactosidase activities were determined. The results are mean values ± the standard deviations of three independent biological replicates. EA, ethyl acetate.