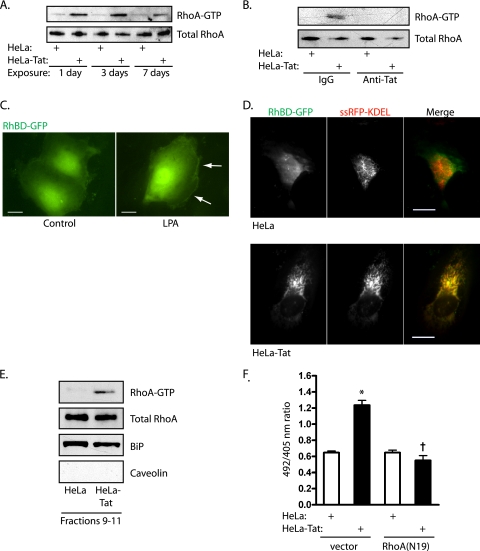
FIG. 5.
Tat activates RhoA on the ER. (A) Pulldowns were used to assess activation of RhoA after 1, 3, and 7 days of exposure to HeLa or HeLa-Tat cells. (B) RhoA activity was assessed by pulldown after 1 day of exposure to HeLa or HeLa-Tat cells in the presence of anti-Tat or control antibodies. (C) HUVEC transfected with RhBD-GFP, to visualize sites of endogenous RhoA-GTP, and stimulated with lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) (10 μM). RhBD-GFP translocated to linear cortical structures (arrows). Scale bar, 20 μm. (D) HUVEC were cotransfected with RhBD-GFP and ssRFP-KDEL, the latter to mark the ER. TIRF imaging revealed typical reticular ventral ER, with nonlocalized RhoA activation after 3 days of exposure to HeLa (top) but extensive relocalization of active RhoA to ER after 3 days of exposure to HeLa-Tat cells. Scale bar, 20 μm. (E) HUVEC were cocultured with HeLa or HeLa-Tat cells for 1 day and subjected to iodixanol density gradient fractionation. Fractions 9 to 11 were pooled and split for immunoblots (RhoA, the ER marker BiP, and the plasma membrane marker caveolin) and for pulldown for active RhoA-GTP. (F) HUVEC were cotransfected with HyPer-ER and either empty vector or RhoA(N19) and cocultured with HeLa or HeLa-Tat cells for 3 days, followed by measurement of 492/405 ratios. The means and SEM of 12 to 15 determinations are shown. *, P < 0.001 from HeLa control; †, P < 0.001 from HeLa-Tat control.