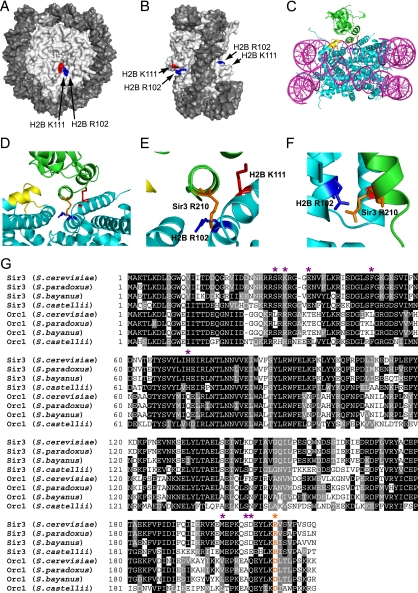
FIG. 8.
(A and B) Location of histone H2B R102 (blue) and H2B K111 (red) residues in the yeast nucleosome crystal structure (1id3 [50]). The image was drawn using POLYVIEW (41). (C to F) Model of histone H2B R102 and K111 interaction with nucleosome-bound Sir3. MacPyMOL (http://www.pymol.org) was used to generate images showing the interaction of histone H2B R102 and K111 with Sir3, based on a published model of Sir3 docking to the yeast nucleosome (35). DNA is in magenta, histone residues are in cyan, and Sir3 protein is in green. The LRS domain is highlighted in yellow, histone H2B R102 is depicted in dark blue, histone H2B K111 is shown in red, and Sir3 R210 is highlighted in orange. Panels D to F are magnified or rotated images of the Sir3-H2B interactions depicted in panel C, with the DNA hidden from view. (G) Sequence alignment of the BAH domain protein sequences of Sir3 and Orc1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Saccharomyces paradoxus, Saccharomyces bayanus, and Saccharomyces castellii. Multiple sequence alignment was performed using CLUSTALW, with default parameters. Sites of orc-like and semi-orc-like suppressor mutants are highlighted with purple asterisks (data from reference 35). The Sir3 R210 residue is highlighted in orange and labeled with an orange asterisk.