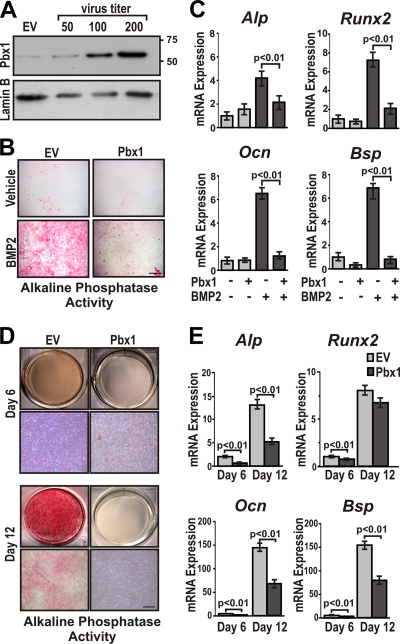
FIG. 3.
Overexpression of Pbx1 results in decreased expression of osteoblast-related genes in mesenchymal progenitor cells. (A) C3H10T1/2 cells were infected with several concentrations (∼50, 100, and 200 PFU/cell) of recombinant lentivirus encoding Pbx1. Relative expression of Pbx1 was determined by Western blotting using an anti-Pbx1 antibody (N-20; Santa Cruz) followed by detection with anti-rabbit-horseradish peroxidase (HRP)/ECL reagent. (B) and C) C3H10T1/2 cells were infected with ∼100 PFU/cell of recombinant lentivirus (EV or Pbx1). Cells were then treated with BMP2 or vehicle (PBS) for 7 days. (B) C3H10T1/2 cells overexpressing Pbx1 demonstrated less alkaline phosphatase activity. Scale bar, 500 μm. (C) Total RNA was isolated from C3H10T1/2 cells, and relative expression of osteoblast-related genes was determined by RT-qPCR using gene-specific primers. (D and E) MC3T3-E1 cells were infected with ∼100 PFU/cell of recombinant lentivirus (EV or Pbx1) and treated with 280 μM ascorbic acid-5 mM β-glycerol phosphate to induce osteogenic differentiation for a period of 6 and 12 days. (D) MC3T3-E1 cells were fixed and stained for alkaline phosphatase activity. (E) Total RNA was isolated from MC3T3-E1 cells, and relative expression of osteoblast-related genes was determined by RT-qPCR using gene-specific primers. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA followed by a Bonferroni posttest. Data are presented as the means from three experiments ± SEM.