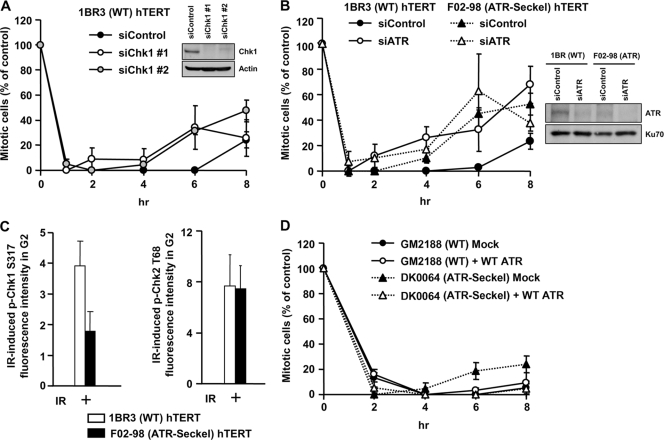
FIG. 2.
ATR-Chk1 signaling contributes to checkpoint maintenance. (A) Mitotic entry in 1BR3 hTERT cells following treatment with control and Chk1 siRNA and 3 Gy IR was examined. Chk1 knockdown did not significantly compromise G2 proportion based on fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis (data not shown). (B) Mitotic entry in 1BR3 hTERT and ATR-SS hTERT cells following treatment with control or ATR siRNA and 3 Gy IR. The right panel shows ATR expression levels. (C) ATR-SS hTERT cells show impaired Chk1 phosphorylation but normal Chk2 phosphorylation. The levels of p-Chk1 Ser317 and p-Chk2 Thr68 were quantified by IF in ATR-SS hTERT G2 cells at 30 min after IR exposure. (D) Mitotic entry in control and ATR-SS LBL cell lines following mock and ATR cDNA transfection. To verify the impact of Chk1 siRNA on Chk1 activity, we examined hydroxyurea (HU)-induced 53BP1 focus formation, which is a characterized Chk1-dependent response (26). 53BP1 foci failed to form after HU treatment in ATR-SS hTERT cells and following Chk1 siRNA, consistent with previous findings (data not shown) (30). Error bars represent the SEM from 3 experiments.