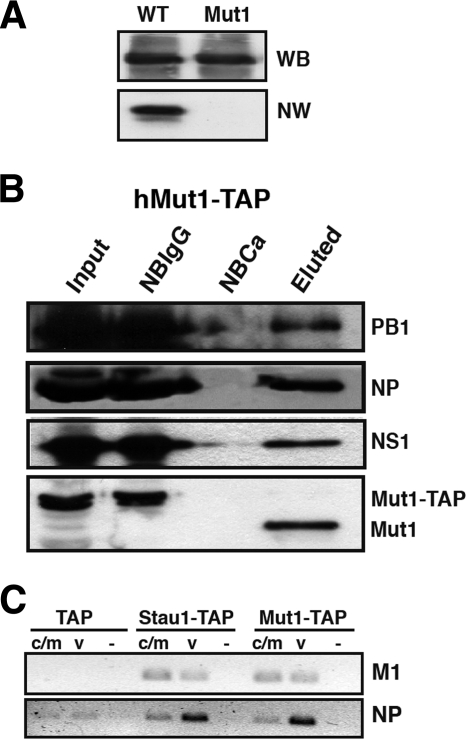
FIG. 3.
Role of hStau1 RBD in the interaction with viral RNPs and RNAs. (A) RNA binding activity of wild-type and Mut1 hStau1 proteins. Equal amounts of either protein, as shown by the Western blot (WB) panel, were used to perform a Northwestern (NW) assay using a probe corresponding to the 3′ UTR of bicoid mRNA. (B) 293T cells were transfected with the plasmid expressing a mutant hStau1-TAP protein (Mut1-TAP) and infected with the influenza virus WSN strain at 24 h posttransfection. Cell extracts were used to perform TAP purification. Aliquots of the total extract (Input), material not bound to IgG-Sepharose resin (NBIgG), material not bound to calmodulin resin (NBCa), and material eluted from the calmodulin resin (Eluted) were analyzed by Western blotting with antibodies specific for PB1, NP, NS1, and hStau1, as indicated on the right. (C) Total RNA was isolated from the eluted fractions shown in panel B, and RT-PCR was performed with primers specific for M1 and NP RNAs of positive (c/m) or negative (v) polarity. Tenfold serial dilutions of the RNAs were analyzed until the PCR signal for the TAP control was negligible. As a negative control, the primers were omitted in the RT reaction step (−) but were included in the PCR step.