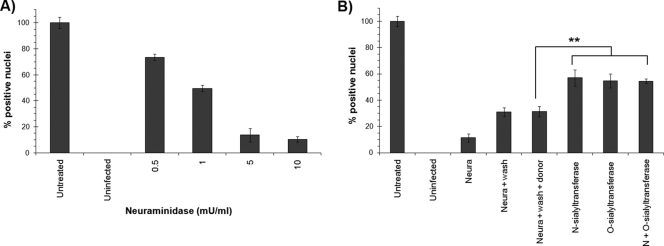
FIG. 2.
PPV binding on the cell surface. (A) PT cells were treated with increasing amounts of neuraminidase in order to remove sialic acid moieties on cell surface glycoproteins. After a wash, PPV was added to the cells for 2 h. Unbound virus was removed by a wash at 2 h p.i., and infection was continued for an additional 18 h. The percentage of infected cells was compared to that of untreated cells (arbitrarily set at 100%) by IF with the capsid-specific antibody 3C9 and DNA staining (Hoechst). (B) Efficiency of infection recovery after neuraminidase treatment followed by specific reconstruction of sialic acids, using O- or N-sialyltransferases, on the cell surface proteins prior to infection. Percentages of infected cells were determined by IF (**, P < 0.004 by the t test).