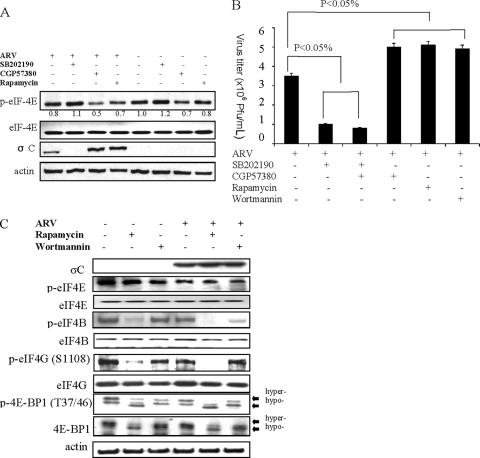
FIG. 7.
Effects of cap-dependent translation inhibitors on ARV replication. DF-1 cells infected with ARV at the dose of 5 PFU/cell. (A) Levels of eIF4E, p-eIF4E, and σC proteins in DF-1 cells treated with 5 μM rapamycin, 10 μM CGP57380, and 5 μM SB202190. At 24 h postinfection the cells were harvested and lysed for Western blot assay. Treatment with 5 μM SB202190 resulted in complete reduction in σC protein expression. (B) Virus titers in DF-1 cells treated with p38 MAPK inhibitor SB202190, Mnk-1 inhibitor CGP57380, and the mTOR inhibitors rapamycin and wortmannin. SB202190 treatment resulted in a 2-fold reduction in ARV titer, while CGP57380, rapamycin, and wortmannin resulted in a slight increase in virus titer compared to untreated cells. (C) Vero cells treated with 5 μM rapamycin and 1 μM wortmannin. Rapamycin treatment caused complete dephosphorylation of eIF4G and eIF4B, as well as partial dephosphorylation of 4E-BP1. The figure is representative from triplicate experiments. Error bars represent standard deviations.