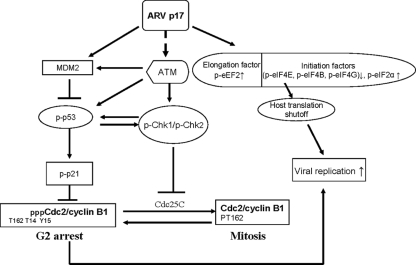
FIG. 9.
Model for the proposed ARV p17 cell cycle regulation. ARV p17 causes G2/M cell cycle arrest through activation of the ATM/p53/p21cip1/waf1/Cdc2 and ATM/Chk1/Chk2/Cdc25C pathways and causes host cellular translation shutoff through a probable checkpoint kinase pathway. p17 increases the levels of phosphorylated ATM, which in turn phosphorylates p53 and Chk1/2. Activation of p53 leads to activation of p21cip1/waf1 that results in cyclin inhibition and hence G2/M cell cycle arrest. Activated Chk2 causes phosphorylation of Cdc25C. Phosphorylated Cdc25C binds to 14-3-3, leading to its sequestration in the cytoplasm, preventing it from activating the Cdc2/cyclin B1 complex. G2/M cell cycle arrest is known to induce host cellular translation shutoff, and ARV p17 transient transfection resulted in the phosphorylation of eEF2 and eIF2α and the dephophosphorylation of Mnk1 and translation initiation factors, leading to host cellular protein translation shutoff. Arrows indicate activation, and blunted lines indicate inhibition.